Using structural information to change the phosphotransfer specificity of a two-component chemotaxis signalling complex
- PMID: 20161720
- PMCID: PMC2817712
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000306
Using structural information to change the phosphotransfer specificity of a two-component chemotaxis signalling complex
Abstract
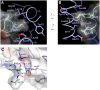
Two-component signal transduction pathways comprising histidine protein kinases (HPKs) and their response regulators (RRs) are widely used to control bacterial responses to environmental challenges. Some bacteria have over 150 different two-component pathways, and the specificity of the phosphotransfer reactions within these systems is tightly controlled to prevent unwanted crosstalk. One of the best understood two-component signalling pathways is the chemotaxis pathway. Here, we present the 1.40 A crystal structure of the histidine-containing phosphotransfer domain of the chemotaxis HPK, CheA(3), in complex with its cognate RR, CheY(6). A methionine finger on CheY(6) that nestles in a hydrophobic pocket in CheA(3) was shown to be important for the interaction and was found to only occur in the cognate RRs of CheA(3), CheY(6), and CheB(2). Site-directed mutagenesis of this methionine in combination with two adjacent residues abolished binding, as shown by surface plasmon resonance studies, and phosphotransfer from CheA(3)-P to CheY(6). Introduction of this methionine and an adjacent alanine residue into a range of noncognate CheYs, dramatically changed their specificity, allowing protein interaction and rapid phosphotransfer from CheA(3)-P. The structure presented here has allowed us to identify specificity determinants for the CheA-CheY interaction and subsequently to successfully reengineer phosphotransfer signalling. In summary, our results provide valuable insight into how cells mediate specificity in one of the most abundant signalling pathways in biology, two-component signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
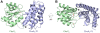
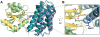
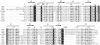


Similar articles
-
Phosphotransfer in Rhodobacter sphaeroides chemotaxis.J Mol Biol. 2002 Nov 15;324(1):35-45. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01031-8. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12421557
-
Chemotaxis in Rhodobacter sphaeroides requires an atypical histidine protein kinase.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 24;279(52):54573-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408855200. Epub 2004 Oct 12. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15485885
-
Modeling chemotaxis reveals the role of reversed phosphotransfer and a bi-functional kinase-phosphatase.PLoS Comput Biol. 2010 Aug 19;6(8):e1000896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000896. PLoS Comput Biol. 2010. PMID: 20808885 Free PMC article.
-
Structural analysis of bacterial chemotaxis proteins: components of a dynamic signaling system.J Struct Biol. 1998 Dec 15;124(2-3):189-200. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1998.4034. J Struct Biol. 1998. PMID: 10049806 Review.
-
Response regulation in bacterial chemotaxis.J Cell Biochem. 1993 Jan;51(1):41-6. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240510109. J Cell Biochem. 1993. PMID: 8381790 Review.
Cited by
-
The structure and dynamic properties of the complete histidine phosphotransfer domain of the chemotaxis specific histidine autokinase CheA from Thermotoga maritima.J Biomol NMR. 2011 Sep;51(1-2):49-55. doi: 10.1007/s10858-011-9540-2. Epub 2011 Sep 27. J Biomol NMR. 2011. PMID: 21947914 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of signaling directionality revealed by 3D snapshots of a kinase:regulator complex in action.Elife. 2016 Dec 12;5:e21422. doi: 10.7554/eLife.21422. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27938660 Free PMC article.
-
A dual binding mode for RhoGTPases in plexin signalling.PLoS Biol. 2011 Aug;9(8):e1001134. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001134. Epub 2011 Aug 30. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21912513 Free PMC article.
-
A Social Medium: ASM's 5th Cell-Cell Communication in Bacteria Meeting in Review.J Bacteriol. 2015 Jul;197(13):2084-2093. doi: 10.1128/JB.00161-15. Epub 2015 Apr 27. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25917904 Free PMC article.
-
Two Proteins Form a Heteromeric Bacterial Self-Recognition Complex in Which Variable Subdomains Determine Allele-Restricted Binding.mBio. 2015 Jun 9;6(3):e00251. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00251-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 26060269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- West A. H, Stock A. M. Histidine kinases and response regulator proteins in two- component signaling systems. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26:369–376. - PubMed
-
- Stock A. M, Robinson V. L, Goudreau P. N. Two-component signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000;69:183–215. - PubMed
-
- Laub M. T, Goulian M. Specificity in two-component signal transduction pathways. Ann Rev Genet. 2007;41:121. - PubMed
-
- Skerker J. M, Prasol M. S, Perchuk B. S, Biondi E. G, Laub M. T. Two-component signal transduction pathways regulating growth and cell cycle progression in a bacterium: a system-level analysis. PLoS Biology. 2005;3:e334. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030334. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

