Vancomycin treatment of infective endocarditis is linked with recently acquired obesity
- PMID: 20161775
- PMCID: PMC2818846
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009074
Vancomycin treatment of infective endocarditis is linked with recently acquired obesity
Abstract
Background: Gut microbiota play a major role in digestion and energy conversion of nutrients. Antibiotics, such as avoparcin (a vancomycin analogue), and probiotics, such as Lactobacillus species, have been used to increase weight in farm animals. We tested the effect of antibiotics given for infective endocarditis (IE) on weight gain (WG).
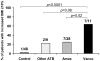
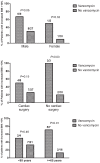
Methodology/principal findings: Forty-eight adults with a definite diagnosis of bacterial IE (antibiotic group) were compared with forty-eight age-matched controls without IE. Their body mass index (BMI) was collected at one month before the first symptoms and one year after hospital discharge. The BMI increased significantly and strongly in vancomycin-plus-gentamycin-treated patients (mean [+/-SE] kg/m(2), +2.3 [0.9], p = 0.03), but not in controls or in patients treated with other antibiotics. Seventeen patients had a BMI increase of >or=10%, and five of the antibiotic group developed obesity. The treatment by vancomycin-plus-gentamycin was an independent predictor of BMI increase of >or=10% (adjusted OR, 6.7; 95% CI, 1.37-33.0; p = 0.02), but not treatment with other antibiotics. Weight gain was particularly high in male patients older than 65 who did not undergo cardiac surgery. Indeed, all three vancomycin-treated patients with these characteristics developed obesity.
Conclusions/significance: A major and significant weight gain can occur after a six-week intravenous treatment by vancomycin plus gentamycin for IE with a risk of obesity, especially in males older than 65 who have not undergone surgery. We speculate on the role of the gut colonization by Lactobacillus sp, a microorganism intrinsically resistant to vancomycin, used as a growth promoter in animals, and found at a high concentration in the feces of obese patients. Thus, nutritional programs and weight follow-up should be utilized in patients under such treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparison of different antibiotic regimens for the treatment of infective endocarditis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 14;5(5):CD009880. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009880.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32407558 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus reuteri and Escherichia coli in the human gut microbiota may predict weight gain associated with vancomycin treatment.Nutr Diabetes. 2013 Sep 9;3(9):e87. doi: 10.1038/nutd.2013.28. Nutr Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 24018615 Free PMC article.
-
[Metabolic side effects of risperidone in early onset schizophrenia].Encephale. 2010 Jun;36(3):242-52. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2009.10.008. Epub 2009 Dec 1. Encephale. 2010. PMID: 20620267 French.
-
Treatment of infective endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: teicoplanin versus vancomycin in a retrospective study.Scand J Infect Dis. 2008;40(6-7):462-7. doi: 10.1080/00365540701837126. Scand J Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18584532
-
Valvular Heart Disease in Adults: Infective Endocarditis.FP Essent. 2017 Jun;457:30-38. FP Essent. 2017. PMID: 28671807 Review.
Cited by
-
Fecal microbiota transplant: benefits and risks.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2015 Feb 4;2(1):ofv005. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofv005. eCollection 2015 Jan. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26034756 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Early Life Antibiotic Exposure Is Not Associated with Growth in Young Children of Vellore, India.J Pediatr. 2015 Nov;167(5):1096-102.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2015.08.015. Epub 2015 Sep 12. J Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 26372535 Free PMC article.
-
Use of antibiotics and risk of type 2 diabetes, overweight and obesity: the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study and the national FINRISK study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Nov 18;22(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-01197-y. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 36401251 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Gut Microbiota in the development of obesity and Diabetes.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Jun 18;15:108. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0278-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 27317359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current and future drug targets in weight management.Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;28(8):1792-818. doi: 10.1007/s11095-010-0341-1. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Pharm Res. 2011. PMID: 21181547 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CL. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. JAMA. 2002;288:1723–1727. - PubMed
-
- Eckel RH, York DA, Rossner S, Hubbard V, Caterson I, et al. Prevention Conference VII: Obesity, a worldwide epidemic related to heart disease and stroke: executive summary. Circulation. 2004;110:2968–2975. - PubMed
-
- Hill JO, Wyatt HR, Reed GW, Peters JC. Obesity and the environment: where do we go from here? Science. 2003;299:853–855. - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Yanovski SZ, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. The epidemiology of obesity. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2087–2102. - PubMed
-
- Christakis NA, Fowler JH. The spread of obesity in a large social network over 32 years. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:370–379. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

