Experimental infection of rabbits with rabbit and genotypes 1 and 4 hepatitis E viruses
- PMID: 20161794
- PMCID: PMC2820092
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009160
Experimental infection of rabbits with rabbit and genotypes 1 and 4 hepatitis E viruses
Abstract
Background: A recent study provided evidence that farmed rabbits in China harbor a novel hepatitis E virus (HEV) genotype. Although the rabbit HEV isolate had 77-79% nucleotide identity to the mammalian HEV genotypes 1 to 4, their genomic organization is very similar. Since rabbits are used widely experimentally, including as models of infection, we investigated whether they constitute an appropriate animal model for human HEV infection.
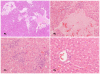
Methods: Forty-two SPF rabbits were divided randomly into eleven groups and inoculated with six different isolates of rabbit HEV, two different doses of a second-passage rabbit HEV, and with genotype 1 and 4 HEV. Sera and feces were collected weekly after inoculation. HEV antigen, RNA, antibody and alanine aminotransferase in sera and HEV RNA in feces were detected. The liver samples were collected during necropsy subject to histopathological examination.
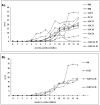
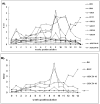
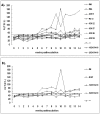
Findings: Rabbits inoculated with rabbit HEV became infected with HEV, with viremia, fecal virus shedding and high serum levels of viral antigens, and developed hepatitis, with elevation of the liver enzyme, ALT. The severity of disease corresponded to the infectious dose (genome equivalents), with the most severe hepatic disease caused by strain GDC54-18. However, only two of nine rabbits infected with HEV genotype 4, and none infected with genotype 1, developed hepatitis although six of nine rabbits inoculated with the genotype 1 HEV and in all rabbits inoculated with the genotype 4 HEV seroconverted to be positive for anti-HEV IgG antibody by 14 weeks post-inoculation.
Conclusions: These data indicate that rabbits are an appropriate model for rabbit HEV infection but are not likely to be useful for the study of human HEV. The rabbit HEV infection of rabbits may provide an appropriate parallel animal model to study HEV pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Infectivity and pathogenicity of different hepatitis E virus genotypes/subtypes in rabbit model.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020 Dec;9(1):2697-2705. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1858178. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020. PMID: 33251979 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental infection of Z:ZCLA Mongolian gerbils with human hepatitis E virus.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 21;21(3):862-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.862. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25624719 Free PMC article.
-
Different susceptibility and pathogenesis of rabbit genotype 3 hepatitis E virus (HEV-3) and human HEV-3 (JRC-HE3) in SPF rabbits.Vet Microbiol. 2017 Aug;207:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.05.019. Epub 2017 May 29. Vet Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28757007
-
An overview: Rabbit hepatitis E virus (HEV) and rabbit providing an animal model for HEV study.Rev Med Virol. 2018 Jan;28(1). doi: 10.1002/rmv.1961. Epub 2017 Nov 17. Rev Med Virol. 2018. PMID: 29148605 Review.
-
Risk of zoonotic transmission of HEV from rabbits.J Clin Virol. 2013 Oct;58(2):357-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2013.02.006. Epub 2013 Mar 7. J Clin Virol. 2013. PMID: 23474012 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cross-species infection of pigs with a novel rabbit, but not rat, strain of hepatitis E virus isolated in the United States.J Gen Virol. 2012 Aug;93(Pt 8):1687-1695. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.041509-0. Epub 2012 Apr 25. J Gen Virol. 2012. PMID: 22535776 Free PMC article.
-
Serological, Virological Investigation and Hepatic Injury Evaluation for Hepatitis E Virus in Hunting Dogs.Pathogens. 2022 Sep 29;11(10):1123. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11101123. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36297180 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Species Transmission of Swine Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 to Rabbits.Viruses. 2020 Jan 2;12(1):53. doi: 10.3390/v12010053. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 31906555 Free PMC article.
-
Host immune status and response to hepatitis E virus infection.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014 Jan;27(1):139-65. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00062-13. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24396140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of hepatitis E virus (HEV) zoonotic transmission: protection of rabbits against HEV challenge following immunization with HEV 239 vaccine.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 30;9(1):e87600. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087600. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24498149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chandra V, Taneja S, Kalia M, Jameel S. Molecular biology and pathogenesis of hepatitis E virus. J Biosci. 2008;33:451–464. - PubMed
-
- Worm HC, van der Poel WH, Brandstatter G. Hepatitis E: an overview. Microbes Infect. 2002;4:657–666. - PubMed
-
- Emerson SU, Purcell RH. Hepatitis E virus. Rev Med Virol. 2003;13:145–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

