A homogenous luminescent proximity assay for 14-3-3 interactions with both phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated client peptides
- PMID: 20161842
- PMCID: PMC2803432
- DOI: 10.2174/1875397300802010040
A homogenous luminescent proximity assay for 14-3-3 interactions with both phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated client peptides
Abstract
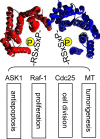
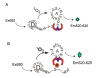
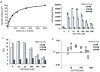
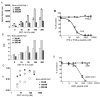
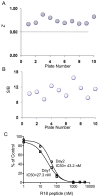
The 14-3-3 proteins are a family of dimeric eukaryotic proteins that mediate both phosphorylation-dependent and -independent protein-protein interactions. Through these interactions, 14-3-3 proteins participate in the regulation of a wide range of cellular processes, including cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and apoptosis. Because of their fundamental importance, 14-3-3 proteins have also been implicated in a variety of diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. In order to monitor 14-3-3/client protein interactions for the discovery of small molecule 14-3-3 modulators, we have designed and optimized 14-3-3 protein binding assays based on the amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay (AlphaScreen) technology. Using the interaction of 14-3-3 with a phosphorylated Raf-1 peptide and a nonphosphorylated R18 peptide as model systems, we have established homogenous "add-and-measure" high-throughput screening assays. Both assays achieved robust performance with S/B ratios above 7 and Z' factors above 0.7. Application of the known antagonistic peptides in our studies further validated the assay for screening of chemical compound libraries to identify small molecules that can modulate 14-3-3 protein-protein interactions.
Keywords: 14-3-3; AlphaScreen; HTS.; protein-protein interaction.
Figures
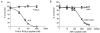

Similar articles
-
The use of AlphaScreen technology in HTS: current status.Curr Chem Genomics. 2008 Feb 25;1:2-10. doi: 10.2174/1875397300801010002. Curr Chem Genomics. 2008. PMID: 20161822 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring 14-3-3 protein interactions with a homogeneous fluorescence polarization assay.J Biomol Screen. 2006 Apr;11(3):269-76. doi: 10.1177/1087057105284862. J Biomol Screen. 2006. PMID: 16699128
-
A time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay for high-throughput screening of 14-3-3 protein-protein interaction inhibitors.Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2013 Jul;11(6):367-81. doi: 10.1089/adt.2013.507. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2013. PMID: 23906346 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-protein interaction modulator drug discovery: past efforts and future opportunities using a rich source of low- and high-throughput screening assays.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2014 Dec;9(12):1393-404. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2014.954544. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2014. PMID: 25374163 Review.
-
Which aspects of HTS are empirically correlated with downstream success?Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2008 May;11(3):327-37. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2008. PMID: 18428086 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of Sanggenon G as a natural cell-permeable small-molecular weight inhibitor of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP).FEBS Open Bio. 2014 Jul 5;4:659-71. doi: 10.1016/j.fob.2014.07.001. eCollection 2014. FEBS Open Bio. 2014. PMID: 25161875 Free PMC article.
-
14-3-3 proteins as potential therapeutic targets.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Sep;22(7):705-12. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.09.012. Epub 2011 Oct 1. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21983031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epilepsy-associated gene Nedd4-2 mediates neuronal activity and seizure susceptibility through AMPA receptors.PLoS Genet. 2017 Feb 17;13(2):e1006634. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006634. eCollection 2017 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28212375 Free PMC article.
-
A Personalized 14-3-3 Disease-Targeting Workflow Yields Repositioning Drug Candidates.Cells. 2025 Apr 8;14(8):559. doi: 10.3390/cells14080559. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40277885 Free PMC article.
-
Two High Throughput Screen Assays for Measurement of TNF-α in THP-1 Cells.Curr Chem Genomics. 2011;5:21-9. doi: 10.2174/1875397301105010021. Epub 2011 May 10. Curr Chem Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21643507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fu H, Subramanian RR, Masters SC. 14-3-3 proteins: structure, function, and regulation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2000;40:617–47. - PubMed
-
- Muslin AJ, Xing H. 14-3-3 proteins: regulation of subcellular localization by molecular interference. Cell Signal. 2000;12(11-12):703–9. - PubMed
-
- Yaffe MB. How do 14-3-3 proteins work?-- Gatekeeper phosphorylation and the molecular anvil hypothesis. FEBS Lett. 2002;513(1):53–7. - PubMed
-
- Aitken A. 14-3-3 proteins: a historic overview. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006;16(3):162–72. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
