Antihyperglycemic effects of separate and composite extract of root of Musa paradisiaca and leaf of Coccinia indica in streptozotocin-induced diabetic male albino rat
- PMID: 20161901
- PMCID: PMC2816485
- DOI: 10.4314/ajtcam.v4i3.31230
Antihyperglycemic effects of separate and composite extract of root of Musa paradisiaca and leaf of Coccinia indica in streptozotocin-induced diabetic male albino rat
Abstract
We evaluated the antihyperglycaemic properties of aqueous-methanolic (40:60) extract of root of Musa paradisiaca and leaf of Coccinia indica in separate as well as in composite manner by conducting experiment on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. We measured food and water intake ability, the fasting blood glucose level, glucose tolerance, activities of important carbohydrate metabolic enzymes like glucose-6-phosphatase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, hexokinase in liver along with quantification of glycogen in liver and in skeletal muscle and serum insulin level. We noted that after treatment of aqueous methanolic extract of above plant parts in separate as well as in composite manner at a concentration of 80 mg/100 g body weight/day to streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat resulted in a significant remedial effect on blood glucose level as well as carbohydrate metabolic enzymes and the quantity of liver and skeletal muscle glycogen. Serum insulin level that was diminished in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat recovered significantly after the co-administration of extract of above plant parts. All the above parameters showed a more potent remedial effect after composite extract treatment with respect to separate treatment and none of the extract has any general metabolic toxicity induction.
Keywords: Coccinia indica; Diabetes; Glycaemic index; Insulin; Musa paradisiaca.
Figures
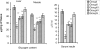
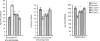
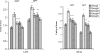
Similar articles
-
Correction of protein metabolic disorders by composite extract of Musa paradisiaca and Coccinia indica in streptozotocin-induced diabetic albino rat: an approach through the pancreas.Pancreas. 2009 Apr;38(3):322-9. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e318192ebdf. Pancreas. 2009. PMID: 19169172
-
Diabetic therapeutic effects of ethyl acetate fraction from the roots of Musa paradisiaca and seeds of Eugenia jambolana in streptozotocin-induced male diabetic rats.Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Nov;31(9):571-84. doi: 10.1358/mf.2009.31.9.1435645. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 20094640
-
Musa paradisiaca L. leaf and fruit peel hydroethanolic extracts improved the lipid profile, glycemic index and oxidative stress in nicotinamide/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Vet Med Sci. 2021 Mar;7(2):500-511. doi: 10.1002/vms3.389. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Vet Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33277985 Free PMC article.
-
Possible Antidiabetic and Antioxidative Activity of Hydro-Methanolic Extract of Musa balbisiana (Colla) Flower in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Male Albino Wistar Strain Rat: A Genomic Approach.Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2019 Feb/Mar;17(2):68-76. doi: 10.1089/adt.2018.889. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2019. PMID: 30869526
-
Protection of testicular dysfunctions by MTEC, a formulated herbal drug, in streptozotocin induced diabetic rat.Biol Pharm Bull. 2007 Jan;30(1):84-90. doi: 10.1248/bpb.30.84. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007. PMID: 17202665
Cited by
-
In silico analysis reveals α-amylase inhibitory potential of Taraxerol (Coccinia indica) and Epoxywithanolide-1 (Withania coagulans): a possible way to control postprandial hyperglycemia-induced endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular events.In Silico Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 9;12(2):82. doi: 10.1007/s40203-024-00257-6. eCollection 2024. In Silico Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39262568
-
Potential antidiabetic phytochemicals in plant roots: a review of in vivo studies.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021 Jul 12;20(2):1837-1854. doi: 10.1007/s40200-021-00853-9. eCollection 2021 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021. PMID: 34900828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioactivity studies on Musa seminifera Lour.Pharmacogn Mag. 2013 Oct;9(36):315-22. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.117827. Pharmacogn Mag. 2013. PMID: 24124283 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of Diabetes mellitus by modulation of GLP-1 via targeting alpha-glucosidase using Acacia tortilis polysaccharide in Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide induced diabetes in rats.J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2020 Oct-Dec;11(4):405-413. doi: 10.1016/j.jaim.2019.06.003. Epub 2020 Nov 2. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2020. PMID: 33153880 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of Musa sp. leaf extracts against multidrug resistant clinical pathogens causing nosocomial infection.Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2013 Sep;3(9):737-42. doi: 10.1016/S2221-1691(13)60148-3. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2013. PMID: 23998016 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akther M H, Mathur M, Vhide N K. Skin and liver toxicity in experimental Lantana camara poisoning in albino rats. Ind J Physiol Pharmacol. 1990;34:13–16. - PubMed
-
- Brugi W, Briner M, Fraken N, Kessler ACH. One step sandwich enzyme immuno assay for insulin using monoclonal antibodies. Clin Biochem. 1988;21:311–314. - PubMed
-
- Can A, Akev N, Ozsoy N, Bolkent S, Arda BP, Yanardag R, Okyar A. Effect of Aloevera leaf gel and pulp extract on the liver in type II diabetic rat models. Biol Pharm Bull. 2004;27:694–698. - PubMed
-
- Chopra RN, Chopra IC, Handa KL, Kapur LD. Medicinal plant in diabetes. In: Gupta P, editor. Indigenous Drug of India. 2nd ed. Calcutta, India: U.N. Dhar & Sons Ltd; 1958. pp. 314–316.
-
- Chou AC, Wilson JE. Carbohydrate metabolism. In: Wood WA, editor. Methods in Enzymol. XIII. New York: Academic Press; 1975. pp. 20–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
