Calyculins and related marine natural products as serine-threonine protein phosphatase PP1 and PP2A inhibitors and total syntheses of calyculin A, B, and C
- PMID: 20161975
- PMCID: PMC2817927
- DOI: 10.3390/md80100122
Calyculins and related marine natural products as serine-threonine protein phosphatase PP1 and PP2A inhibitors and total syntheses of calyculin A, B, and C
Abstract
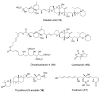
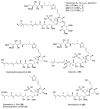
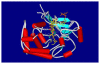
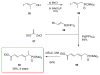
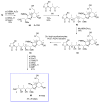
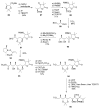
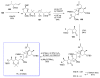
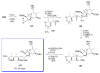
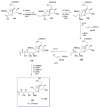
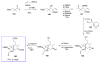
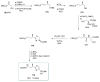
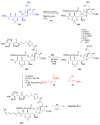
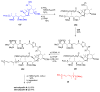
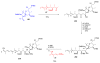
Calyculins, highly cytotoxic polyketides, originally isolated from the marine sponge Discodermia calyx by Fusetani and co-workers, belong to the lithistid sponges group. These molecules have become interesting targets for cell biologists and synthetic organic chemists. The serine/threonine protein phosphatases play an essential role in the cellular signalling, metabolism, and cell cycle control. Calyculins express potent protein phosphatase 1 and 2A inhibitory activity, and have therefore become valuable tools for cellular biologists studying intracellular processes and their control by reversible phosphorylation. Calyculins might also play an important role in the development of several diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and type 2-diabetes mellitus. The fascinating structures of calyculins have inspired various groups of synthetic organic chemists to develop total syntheses of the most abundant calyculins A and C. However, with fifteen chiral centres, a cyano-capped tetraene unit, a phosphate-bearing spiroketal, an anti, anti, anti dipropionate segment, an alpha-chiral oxazole, and a trihydroxylated gamma-amino acid, calyculins reach versatility that only few natural products can surpass, and truly challenge modern chemists' asymmetric synthesis skills.
Keywords: marine natural products; protein phosphatase inhibitors; total synthesis.
Figures

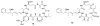
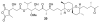



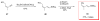






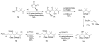
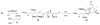

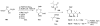

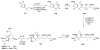
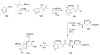

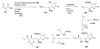

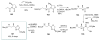


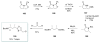
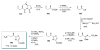


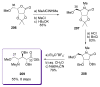

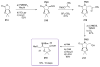
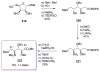
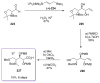

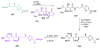

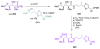
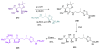


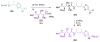


References
-
- Nakao Y, Fusetani N. Enzyme inhibitors from marine invertebrates. J Nat Prod. 2007;70:689–710. - PubMed
-
- Barford D, Das AK, Egloff M-P. The strucrure and mechanism of protein phosphatases: Insights into catalysis and regulation. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1998;27:133–164. - PubMed
-
- Cohen PTW. Novel protein serine/threonine phosphatases: Variety is the spice of life. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997;22:245–251. - PubMed
-
- McCluskey A, Sim ATR, Sakoff JA. Serine-Threonine protein phosphatase inhibitors: Development of potential therapeutic strategies. J Med Chem. 2002;45:1151–1175. - PubMed
-
- Schönthal AH. Role of serine/threonine protein phosphatase 2A in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2001;170:1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
