Nanoparticulate Quillaja saponin induces apoptosis in human leukemia cell lines with a high therapeutic index
- PMID: 20161987
- PMCID: PMC2819906
Nanoparticulate Quillaja saponin induces apoptosis in human leukemia cell lines with a high therapeutic index
Abstract
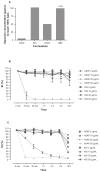
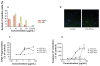
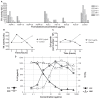
Saponin fractions of Quillaja saponaria Molina (QS) have cytotoxic activity against cancer cells in vitro, but are too toxic to be useful in the clinic. The toxic effect was abolished by converting QS fractions into stable nanoparticles through the binding of QS to cholesterol. Two fractions of QS were selected for particle formation, one with an acyl-chain (ASAP) was used to form killing and growth-inhibiting (KGI) particles, and the other without the acyl-chain (DSAP) was used to formulate blocking and balancing effect (BBE) particles. KGI showed significant growth inhibiting and cancer cell-killing activities in nine of 10 cell lines while BBE showed that on one cell line. The monoblastoid lymphoma cell line U937 was selected for analyzing the mode of action. Low concentrations of KGI (0.5 and 2 microg/mL) induced irreversible exit from the cell cycle, differentiation measured by cytokine production, and eventually programmed cell death (apoptosis). Compared to normal human monocytes, the U937 cells were 30-fold more sensitive to KGI. The nontoxic BBE blocked the cell killing effect of KGI in a concentration-dependent manner. In conclusion, the formulation of QS into nanoparticles has the potential of becoming a new class of anticancer agents.
Keywords: Quillaja saponin; anticancer drug; apoptosis; nanoparticle.
Figures



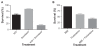
Similar articles
-
The nanoparticulate Quillaja saponin KGI exerts anti-proliferative effects by down-regulation of cell cycle molecules in U937 and HL-60 human leukemia cells.Leuk Lymphoma. 2014 Jul;55(7):1618-24. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.853301. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014. PMID: 24138332
-
The Nanoparticulate Quillaja Saponin BBE is selectively active towards renal cell carcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2013 Jan;33(1):143-51. Anticancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23267139
-
Hierarchical high internal phase emulsions and transparent oleogels stabilized by quillaja saponin-coated nanodroplets for color performance.Food Funct. 2017 Feb 22;8(2):823-831. doi: 10.1039/c6fo01752e. Food Funct. 2017. PMID: 28124036
-
Foamy matters: an update on Quillaja saponins and their use as immunoadjuvants.Future Med Chem. 2019 Jun;11(12):1485-1499. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2018-0438. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Future Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31304830 Review.
-
Quillaja Saponin Characteristics and Functional Properties.Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2019 Mar 25;10:43-73. doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-032818-122010. Epub 2019 Jan 21. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2019. PMID: 30664381 Review.
Cited by
-
High toxicity and specificity of the saponin 3-GlcA-28-AraRhaxyl-medicagenate, from Medicago truncatula seeds, for Sitophilus oryzae.BMC Chem Biol. 2012 Jul 2;12:3. doi: 10.1186/1472-6769-12-3. BMC Chem Biol. 2012. PMID: 22536832 Free PMC article.
-
Saponins from Quillaja saponaria and Quillaja brasiliensis: Particular Chemical Characteristics and Biological Activities.Molecules. 2019 Jan 4;24(1):171. doi: 10.3390/molecules24010171. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30621160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Saponin Facilitates Anti-Robo1 Immunotoxin Cytotoxic Effects on Maxillary Sinus Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Oncol. 2020 Mar 11;2020:9593516. doi: 10.1155/2020/9593516. eCollection 2020. J Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32256588 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro anti‑bacterial activity of diosgenin on Porphyromonas gingivalis and Prevotella intermedia.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Dec;22(6):5392-5398. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11620. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 33174005 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation technologies for oral vaccines.Clin Exp Immunol. 2019 Nov;198(2):153-169. doi: 10.1111/cei.13352. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Clin Exp Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31318446 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nygren P, Larsson R. Overview of the clinical efficacy of investigational anticancer drugs. J Intern Med. 2003;253(1):46–75. - PubMed
-
- Kerwin SM. Soy saponins and the anticancer effects of soybeans and soy-based foods. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2004;4(3):263–272. - PubMed
-
- Rao AV, Sung MK. Saponins as anticarcinogens. J Nutr. 1995;125(3 Suppl):717S–724S. - PubMed
-
- Tian F, Zhang X, Tong Y, et al. PE, a new sulfated saponin from sea cucumber, exhibits anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activities in vitro andin vivo. Cancer Biol Ther. 2005;4(8):874–882. - PubMed
-
- Tin MM, Cho CH, Chan K, James AE, Ko JK. Astragalus saponins induce growth inhibition and apoptosis in human colon cancer cells and tumor xenograft. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28(6):1347–1355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

