Chalcones enhance TRAIL-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 20161998
- PMCID: PMC2820986
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms11010001
Chalcones enhance TRAIL-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
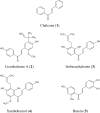
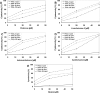
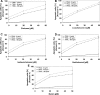
Chalcones exhibit chemopreventive and antitumor effects. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a naturally occurring anticancer agent that induces apoptosis in cancer cells and is not toxic to normal cells. We examined the cytotoxic and apoptotic effect of five chalcones in combination with TRAIL on prostate cancer cells. The cytotoxicity was evaluated by the MTT and LDH assays. The apoptosis was determined using flow cytometry with annexin V-FITC. Our study showed that all five tested chalcones: chalcone, licochalcone-A, isobavachalcone, xanthohumol, butein markedly augmented TRAIL-mediated apoptosis and cytotoxicity in prostate cancer cells and confirmed the significant role of chalcones in chemoprevention of prostate cancer.
Keywords: TRAIL (tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand); apoptosis; chalcones; chemoprevention; prostate cancer.
Figures
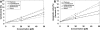

Similar articles
-
Chalcones and dihydrochalcones augment TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in prostate cancer cells.Molecules. 2010 Aug 4;15(8):5336-53. doi: 10.3390/molecules15085336. Molecules. 2010. PMID: 20714300 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting death receptor TRAIL-R2 by chalcones for TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Nov 20;13(11):15343-59. doi: 10.3390/ijms131115343. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23203129 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanolic extract of Brazilian green propolis sensitizes prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis.Int J Oncol. 2011 Apr;38(4):941-53. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.930. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Int J Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21286663
-
The role of dietary polyphenols in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis for cancer chemoprevention.Eur J Cancer Prev. 2011 Jan;20(1):63-9. doi: 10.1097/CEJ.0b013e32833ecc48. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2011. PMID: 20861738 Review.
-
[Role of TRAIL in the treatment of prostate cancer: An update].Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2015 Oct;21(10):941-4. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2015. PMID: 26665687 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Synergistic Proliferation Effects of Xanthohumol and Niflumic Acid on Merkel and Glioblastoma Cancer Cells: Role of Cell Membrane Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 13;25(20):11015. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011015. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456799 Free PMC article.
-
NutriTRAILomics in prostate cancer: time to have two strings to one's bow.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Apr;39(4):4909-14. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-1286-0. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22143879 Review.
-
Chlorin-based photodynamic therapy enhances the effect of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in bladder cancer cells.Med Sci Monit. 2012 Jan;18(1):BR47-53. doi: 10.12659/msm.882203. Med Sci Monit. 2012. PMID: 22207109 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ALA-mediated photodynamic therapy in combination with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) on bladder cancer cells.Cent European J Urol. 2011;64(3):175-9. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2011.03.art18. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Cent European J Urol. 2011. PMID: 24578888 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of inflammatory mediators by neobavaisoflavone in activated RAW264.7 macrophages.Molecules. 2011 May 3;16(5):3701-12. doi: 10.3390/molecules16053701. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 21540797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dicarlo G, Mascolo N, Izzo AA, Capasso F. Flavonoids: Old and new aspects of class of natural therapeutic drugs. Life Sci. 1999;65:337–353. - PubMed
-
- Dimmock JR, Elias DW, Beazely MA, Kandepu NM. Bioactivities of chalcones. Curr. Med. Chem. 1999;6:1125–1149. - PubMed
-
- Go ML, Wu X, Liu XL. Chalcones: An update on cytotoxic and chemopreventive properties. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005;12:481–499. - PubMed
-
- Nowakowska Z. A review of anti-infective and anti-inflammatory chalcones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007;42:125–137. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

