Evaluation of the antioxidant effects of Ziziphus mauritiana Lam. Leaf extracts against chronic ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity in rat liver
- PMID: 20162053
- PMCID: PMC2816599
- DOI: 10.4314/ajtcam.v5i1.31254
Evaluation of the antioxidant effects of Ziziphus mauritiana Lam. Leaf extracts against chronic ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity in rat liver
Abstract
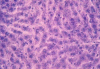
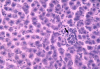
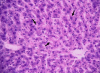
Chronic alcohol ingestion is known to increase the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby leading to liver damage. Antioxidant enzymes act individually or in combination to reduce or counter the effect of these ROS. Chronic administration of alcohol at (40% v/v, 1 ml/100 g), for 6 weeks showed a significant (p<0.05) elevated levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and total bilirubin (TB). There was also a significant (p<0.05) decreased levels of catalase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase and superoxide dismutase compared to control rats. Pre-treatment of rats with 200, 400 mg/kg body weight of aqueous leaf extract of Ziziphus mauritiana or 100 mg/kg silymarin resulted in a significant (p<0.05) decreased levels of ALT, AST, ALP, and TB with levels of catalase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase and superoxide dismutase showing a significant (p<0.05) increase compared to group administered alcohol only. Histopathology of rat liver administered with alcohol only resulted in severe necrosis, mononuclear cell aggregation and fatty degeneration in the central and mid zonal areas which was a characteristic of a damaged liver. Pre-treatment with the aqueous extract of Ziziphus mauritiana or silymarin reduced the morphological changes that are associated with chronic alcohol administration. The presence of tannins, saponins and phenolic compounds observed in the plant extract could be responsible for the observed effects of decreasing the levels of injured tissue marker and lipid peroxidation.
Keywords: Antioxidant enzymes; Ziziphus mauritiana; alcohol; liver damage.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Crinum jagus (J. Thomps. Dandy): Antioxidant and protective properties as a medicinal plant on toluene-induced oxidative stress damages in liver and kidney of rats.Toxicol Rep. 2022 Mar 29;9:699-712. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.03.026. eCollection 2022. Toxicol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35433275 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of root and stem bark of wild medicinal plant Ziziphus mauritiana (Lamk.) against silica induced toxicity in Wistar albino rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Oct 5;224:111-118. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.04.045. Epub 2018 May 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29727735
-
White butterfly (Clerodendrum volubile) leaf extract protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Dec;96:924-929. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.005. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 29224792
-
Biochemical and molecular modulation of CCl4-induced peripheral and central damage by Tilia americana var. mexicanaextracts.Saudi Pharm J. 2017 Mar;25(3):319-331. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2016.06.008. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Saudi Pharm J. 2017. PMID: 28344485 Free PMC article.
-
Hot aqueous leaf extract of Lasianthera africana (Icacinaceae) attenuates rifampicin-isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity.J Integr Med. 2018 Jul;16(4):263-272. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 8. J Integr Med. 2018. PMID: 29776838
Cited by
-
The Effects of Syzygium samarangense, Passiflora edulis and Solanum muricatum on Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 26;17(10):1616. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101616. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27681723 Free PMC article.
-
Phenolic Profile of Seedless Ziziphus mauritiana Fruits and Leaves Extracts with In Vivo Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities: Influence on Pro-Inflammatory Mediators.Chem Biodivers. 2025 Mar;22(3):e202401728. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202401728. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Chem Biodivers. 2025. PMID: 39475065 Free PMC article.
-
Ziziphus mauritiana Lam. Bark and Leaves: Extraction, Phytochemical Composition, In Vitro Bioassays and In Silico Studies.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 8;13(16):2195. doi: 10.3390/plants13162195. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204631 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory, Cytotoxicity, and Antioxidant Activities of Roots of Ziziphus mauritiana.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Jul;13(Suppl 2):S262-S265. doi: 10.4103/pm.pm_398_16. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 28808390 Free PMC article.
-
Suaeda vermiculata Aqueous-Ethanolic Extract-Based Mitigation of CCl4-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats, and HepG-2 and HepG-2/ADR Cell-Lines-Based Cytotoxicity Evaluations.Plants (Basel). 2020 Sep 29;9(10):1291. doi: 10.3390/plants9101291. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33003604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arteel GE. Oxidants and antioxidants in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterol. 2003;124:778–790. - PubMed
-
- Arti A, Byren TM, Nair MG. Modulation of liposomal membrane fluidity by flavonoids and isoflavonoids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000;373:102–109. - PubMed
-
- Dahiru D, Sini JM, John-Africa L. Antidiarrhoeal activity of Ziziphus mauritiana root extract in rodents. Afr J Biotechnol. 2006;5(10):941–945.
-
- Dahiru D, William ET, Nadro MS. Protective effect of Ziziphus mauritiana leaf extract on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury. Afr J Biotechnol. 2005;4(10):1177–1179.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
