Meiotic silencing and fragmentation of the male germline restricted chromosome in zebra finch
- PMID: 20162291
- PMCID: PMC2875885
- DOI: 10.1007/s00412-010-0258-9
Meiotic silencing and fragmentation of the male germline restricted chromosome in zebra finch
Abstract
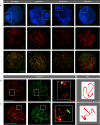
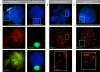
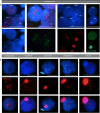
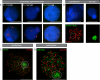
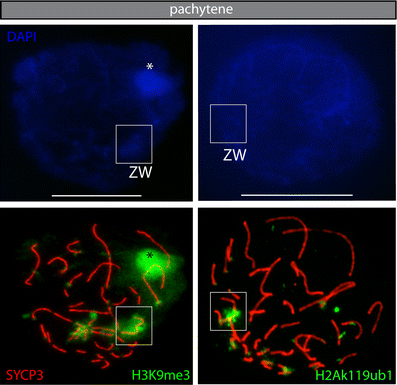
During male meiotic prophase in mammals, X and Y are in a largely unsynapsed configuration, which is thought to trigger meiotic sex chromosome inactivation (MSCI). In avian species, females are ZW, and males ZZ. Although Z and W in chicken oocytes show complete, largely heterologous synapsis, they too undergo MSCI, albeit only transiently. The W chromosome is already inactive in early meiotic prophase, and inactive chromatin marks may spread on to the Z upon synapsis. Mammalian MSCI is considered as a specialised form of the general meiotic silencing mechanism, named meiotic silencing of unsynapsed chromatin (MSUC). Herein, we studied the avian form of MSUC, by analysing the behaviour of the peculiar germline restricted chromosome (GRC) that is present as a single copy in zebra finch spermatocytes. In the female germline, this chromosome is present in two copies, which normally synapse and recombine. In contrast, during male meiosis, the single GRC is always eliminated. We found that the GRC in the male germline is silenced from early leptotene onwards, similar to the W chromosome in avian oocytes. The GRC remains largely unsynapsed throughout meiotic prophase I, although patches of SYCP1 staining indicate that part of the GRC may self-synapse. In addition, the GRC is largely devoid of meiotic double strand breaks. We observed a lack of the inner centromere protein INCENP on the GRC and elimination of the GRC following metaphase I. Subsequently, the GRC forms a micronucleus in which the DNA is fragmented. We conclude that in contrast to MSUC in mammals, meiotic silencing of this single chromosome in the avian germline occurs prior to, and independent of DNA double strand breaks and chromosome pairing, hence we have named this phenomenon meiotic silencing prior to synapsis (MSPS).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

