Cleavage of galectin-3 by matrix metalloproteases induces angiogenesis in breast cancer
- PMID: 20162566
- PMCID: PMC3334857
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.25254
Cleavage of galectin-3 by matrix metalloproteases induces angiogenesis in breast cancer
Abstract
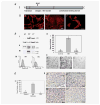
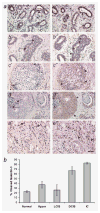
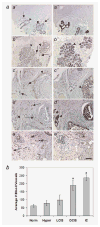
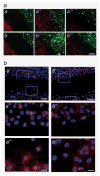
Galectin-3 cleavage is related to progression of human breast and prostate cancer and is partly responsible for tumor growth, angiogenesis and apoptosis resistance in mouse models. A functional polymorphism in galectin-3 gene, determining its susceptibility to cleavage by matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)-2/-9 is related to racial disparity in breast cancer incidence in Asian and Caucasian women. The purpose of our study is to evaluate (i) if cleavage of galectin-3 could be related to angiogenesis during the progression of human breast cancer, (ii) the role of cleaved galectin-3 in induction of angiogenesis and (iii) determination of the galectin-3 domain responsible for induction of angiogenic response. Galectin-3 null breast cancer cells BT-459 were transfected with either cleavable full-length galectin-3 or its fragmented peptides. Chemotaxis, chemoinvasion, heterotypic aggregation, epithelial-endothelial cell interactions and angiogenesis were compared to noncleavable galectin-3. BT-549-H(64) cells harboring cleavable galectin-3 exhibited increased chemotaxis, invasion and interactions with endothelial cells resulting in angiogenesis and 3D morphogenesis compared to BT-549-P(64) cells harboring noncleavable galectin-3. BT-549-H(64) cells induced increased migration and phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase in migrating endothelial cells. Endothelial cells cocultured with BT-549 cells transfected with galectin-3 peptides indicate that amino acids 1-62 and 33-250 stimulate migration and morphogenesis of endothelial cells. Immunohistochemical analysis of blood vessel density and galectin-3 cleavage in a breast cancer progression tissue array support the in vitro findings. We conclude that the cleavage of the N terminus of galectin-3 followed by its release in the tumor microenvironment in part leads to breast cancer angiogenesis and progression.
Figures


References
-
- Barondes SH, Cooper DN, Gitt MA, Leffler H. Galectins. Structure and function of a large family of animal lectins. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:20807–10. - PubMed
-
- Lotan R, Raz A. Low colony formation in vivo and in culture as exhibited by metastatic melanoma cells selected for reduced homotypic aggregation. Cancer Res. 1983;43:2088–93. - PubMed
-
- Meromsky L, Lotan R, Raz A. Implications of endogenous tumor cell surface lectins as mediators of cellular interactions and lung colonization. Cancer Res. 1986;46:5270–5. - PubMed
-
- Dumic J, Dabelic S, Flogel M. Galectin-3: an open-ended story. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1760:616–35. - PubMed
-
- Gong HC, Honjo Y, Nangia-Makker P, Hogan V, Mazurak N, Bresalier RS, Raz A. The NH2 terminus of galectin-3 governs cellular compartmentalization and functions in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1999;59:6239–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
