Radiation monotherapy as regional treatment for lymph node-positive Merkel cell carcinoma
- PMID: 20162707
- PMCID: PMC9439996
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.24919
Radiation monotherapy as regional treatment for lymph node-positive Merkel cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: : Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is an aggressive cutaneous malignancy with a high risk of lymph node involvement. To the authors' knowledge, few data have been published to date regarding the optimal regional therapy for lymph node-positive patients. This cohort study was performed to analyze the outcomes of patients with lymph node-positive MCC treated with lymph node irradiation as definitive therapy compared with completion lymphadenectomy (CLND).
Methods: : Fifty patients with lymph node involvement of MCC at presentation and adequate follow-up data were included in this analysis. Forty-three of these patients were enrolled and followed prospectively. Twenty-six patients presented with microscopic lymph node disease, and 24 patients presented with palpable lymph node involvement.
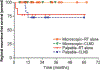
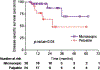
Results: : Regional control for patients with microscopically involved lymph nodes was 100% regardless of treatment modality-definitive lymph node irradiation (n = 19) or CLND +/- radiotherapy (n = 7) with median follow-up of 18 months. Patients with clinically positive lymph nodes had 2-year regional recurrence-free survival rate of 78% and 73% in the definitive lymph node irradiation (n = 9) and CLND +/- radiotherapy (n = 15) groups, respectively (P = .8) with a median follow-up of 16 months.
Conclusions: : To the best of the authors' knowledge, the current study is the largest series published to date of radiation monotherapy as regional treatment for lymph node-positive MCC. Lymph node irradiation alone to positive regional lymph nodes was found to confer an excellent regional control rate that was comparable to CLND for both microscopic and palpable lymph node disease. There was no difference noted with regard to overall survival. Given their similar efficacy, the choice between these lymph node therapies may be based on the clinical scenario and anticipated side effect profiles. Cancer 2010. (c) 2010 American Cancer Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Radiation versus resection for Merkel cell carcinoma.Cancer. 2010 Apr 1;116(7):1620-2. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24931. Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20108304 No abstract available.
References
-
- Engels EA, Frisch M, Goedert JJ, Biggar RJ, Miller RW. Merkel cell carcinoma and HIV infection. Lancet. 2002; 359:497–498. - PubMed
-
- Penn I, First MR. Merkel’s cell carcinoma in organ recipients: report of 41 cases. Transplantation. 1999;68:1717–1721. - PubMed
-
- Allen PJ, Bowne WB, Jaques DP, Brennan MF, Busam K, Coit DG. Merkel cell carcinoma: prognosis and treatment of patients from a single institution. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:2300–2309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

