Uric acid and antioxidant effects of wine
- PMID: 20162741
- PMCID: PMC2829179
- DOI: 10.3325/cmj.2010.51.16
Uric acid and antioxidant effects of wine
Abstract
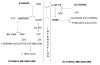
The aim of this article is to review the role of uric acid in the context of antioxidant effects of wine and its potential implication to human health. We described and discussed the mechanisms of increase in plasma antioxidant capacity after consumption of moderate amounts of wine. Because this effect is largely contributed by acute elevation in plasma uric acid, we paid special attention to wine constituents and metabolic processes that are likely to be involved in uric acid elevation.
Figures
References
-
- Athyros VG, Liberopoulos EN, Mikhailidis DP, Papageorgiou AA, Ganotakis ES, Tziomalos K, et al. Association of drinking pattern and alcohol beverage type with the prevalence of metabolic syndrome, diabetes, coronary heart disease, stroke, and peripheral arterial disease in a Mediterranean cohort. Angiology. 2007;58:689–97. doi: 10.1177/0003319707306146. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

