Decreased arteriolar tetrahydrobiopterin is linked to superoxide generation from nitric oxide synthase in mice fed high salt
- PMID: 20163541
- PMCID: PMC3402363
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1549-8719.2009.00014.x
Decreased arteriolar tetrahydrobiopterin is linked to superoxide generation from nitric oxide synthase in mice fed high salt
Abstract
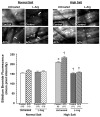
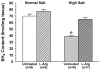
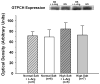
Objective: Impaired endothelium-dependent arteriolar dilation in mice fed high salt (HS) is due to local oxidation of nitric oxide (NO) by superoxide anion (O(2) (-)). We explored the possibility that "uncoupled" endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) is the source of this O(2) (-).
Methods: Levels of L-arginine (L-Arg), tetrahydrobiopterin (BH(4)), and O(2) (-) (hydroethidine oxidation) were measured in spinotrapezius muscle arterioles of mice fed normal salt (0.45%, NS) or (4%, HS) diets for 4 weeks, with or without dietary L-Arg supplementation. The contribution of NO to endothelium-dependent dilation was determined from the effect of N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) on responses to acetylcholine (ACh).
Results: Arterioles in HS mice had lower [BH(4)] and higher O(2) (-) levels than those in NS mice. ACh further increased arteriolar O(2) (-) in HS mice only. L-Arg supplementation prevented the reduction in [BH(4)] in arterioles of HS mice, and O(2) (-) was not elevated in these vessels. Compared to NS mice, arteriolar ACh responses were diminished and insensitive to L-NAME in HS mice, but not in HS mice supplemented with L-Arg.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that eNOS uncoupling due to low [BH(4)] is responsible for O(2) (-) generation and reduced NO-dependent dilation in arterioles of mice fed a HS diet.
Figures





Similar articles
-
High salt intake reduces endothelium-dependent dilation of mouse arterioles via superoxide anion generated from nitric oxide synthase.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007 Apr;292(4):R1550-6. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00703.2006. Epub 2006 Nov 30. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17138723
-
Lack of nitric oxide mediation of flow-dependent arteriolar dilation in type I diabetes is restored by sepiapterin.J Vasc Res. 2003 Jan-Feb;40(1):47-57. doi: 10.1159/000068938. J Vasc Res. 2003. PMID: 12644725
-
Caloric restriction reverses high-fat diet-induced endothelial dysfunction and vascular superoxide production in C57Bl/6 mice.Heart Vessels. 2010 May;25(3):254-62. doi: 10.1007/s00380-009-1182-x. Epub 2010 May 29. Heart Vessels. 2010. PMID: 20512454
-
Ageing diminishes endothelium-dependent vasodilatation and tetrahydrobiopterin content in rat skeletal muscle arterioles.J Physiol. 2008 Feb 15;586(4):1161-8. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.147686. Epub 2007 Dec 6. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18063659 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced arteriolar responses to skeletal muscle contraction after ingestion of a high salt diet.J Vasc Res. 2005 May-Jun;42(3):226-36. doi: 10.1159/000085461. Epub 2005 Apr 25. J Vasc Res. 2005. PMID: 15855795
Cited by
-
Understanding the Two Faces of Low-Salt Intake.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017 Jun;19(6):49. doi: 10.1007/s11906-017-0744-z. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017. PMID: 28501983 Review.
-
Early developmental conditioning of later health and disease: physiology or pathophysiology?Physiol Rev. 2014 Oct;94(4):1027-76. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00029.2013. Physiol Rev. 2014. PMID: 25287859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High dietary sodium intake impairs endothelium-dependent dilation in healthy salt-resistant humans.J Hypertens. 2013 Mar;31(3):530-6. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e32835c6ca8. J Hypertens. 2013. PMID: 23263240 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular effects of dietary salt.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2015 Jan;24(1):8-13. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000089. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 25415615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effect of Xin-Ji-Er-Kang on cardiovascular remodeling in high salt-induced hypertensive mice.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Mar;17(3):1551-1562. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.7105. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 30783421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagi Z, Koller A. Lack of nitric oxide mediation of flow-dependent arteriolar dilation in Type 1 diabetes is restored by sepiapterin. J Vasc Res. 2003;40:47–57. - PubMed
-
- Bendall JK, Alp NJ, Warrick N, Cai S, Adlam D, Rockett K, Yokoyama M, Kawashima S, Channon KM. Stoichiometric relationships between endothelial tetrahydrobiopterin, endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) activity, and eNOS coupling in vivo: insights from transgenic mice with endothelial-targeted GTP cyclohydrolase 1 and eNOS overexpression. Circ Res. 2005;97:864–71. - PubMed
-
- Benov L, Sztejnberg L, Fridovich I. Critical evaluation of the use of hydroethidine as a measure of superoxide anion radical. Free Radic Biol Med. 1998;25:826–831. - PubMed
-
- Boegehold MA. Effect of dietary salt on arteriolar nitric oxide in striated muscle of normotensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 1993;264:H1810–H1816. - PubMed
-
- Boegehold MA. Flow-dependent arteriolar dilation in normotensive rats fed low- or high-salt diets. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 1995;269:H1407–H1414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

