Legionella pneumophila promotes functional interactions between plasma membrane syntaxins and Sec22b
- PMID: 20163564
- PMCID: PMC3164831
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01050.x
Legionella pneumophila promotes functional interactions between plasma membrane syntaxins and Sec22b
Abstract
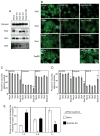
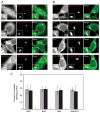
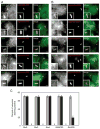
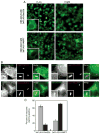
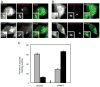
Biogenesis of a specialized organelle that supports intracellular replication of Legionella pneumophila involves the fusion of secretory vesicles exiting the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) with phagosomes containing this bacterial pathogen. Here, we investigated host plasma membrane SNARE proteins to determine whether they play a role in trafficking of vacuoles containing L. pneumophila. Depletion of plasma membrane syntaxins by RNA interference resulted in delayed acquisition of the resident ER protein calnexin and enhanced retention of Rab1 on phagosomes containing virulent L. pneumophila, suggesting that these SNARE proteins are involved in vacuole biogenesis. Plasma membrane-localized SNARE proteins syntaxin 2, syntaxin 3, syntaxin 4 and SNAP23 localized to vacuoles containing L. pneumophila. The ER-localized SNARE protein Sec22b was found to interact with plasma membrane SNAREs on vacuoles containing virulent L. pneumophila, but not on vacuoles containing avirulent mutants of L. pneumophila. The addition of alpha-SNAP and N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (NSF) to the plasma membrane SNARE complexes formed by virulent L. pneumophila resulted in the dissociation of Sec22b, indicating functional pairing between these SNAREs. Thus, L. pneumophila stimulates the non-canonical pairing of plasma membrane t-SNAREs with the v-SNARE Sec22b to promote fusion of the phagosome with ER-derived vesicles. The mechanism by which L. pneumophila promotes pairing of plasma membrane syntaxins and Sec22b could provide unique insight into how the secretory vesicles could provide an additional membrane reserve subverted during phagosome maturation.
Figures

References
-
- Kagan JC, Roy CR. Legionella phagosomes intercept vesicular traffic from endoplasmic reticulum exit sites. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:945–954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

