Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 enhances survival of LX2 human hepatic stellate cells
- PMID: 20163708
- PMCID: PMC2834615
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-1536-3-3
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 enhances survival of LX2 human hepatic stellate cells
Abstract
Background: Expression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 (IGFBP5) is strongly induced upon activation of hepatic stellate cells and their transdifferentiation into myofibroblasts in vitro. This was confirmed in vivo in an animal model of liver fibrosis. Since IGFBP5 has been shown to promote fibrosis in other tissues, the aim of this study was to investigate its role in the progression of liver fibrosis.
Methods: The effect of IGFBP5 was studied in LX2 cells, a model for partially activated hepatic stellate cells, and in human primary liver myofibroblasts. IGFBP5 signalling was modulated by the addition of recombinant protein, by lentiviral overexpression, and by siRNA mediated silencing. Furthermore, the addition of IGF1 and silencing of the IGF1R was used to investigate the role of the IGF-axis in IGFBP5 mediated effects.
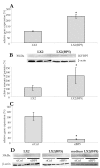
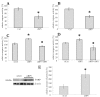
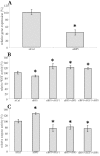
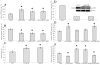
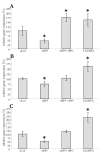
Results: IGFBP5 enhanced the survival of LX2 cells and myofibroblasts via a >50% suppression of apoptosis. This effect of IGFBP5 was not modulated by the addition of IGF1, nor by silencing of the IGF1R. Additionally, IGFBP5 was able to enhance the expression of established pro-fibrotic markers, such as collagen Ialpha1, TIMP1 and MMP1.
Conclusion: IGFBP5 enhances the survival of (partially) activated hepatic stellate cells and myofibroblasts by lowering apoptosis via an IGF1-independent mechanism, and enhances the expression of profibrotic genes. Its lowered expression may, therefore, reduce the progression of liver fibrosis.
Figures
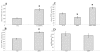
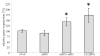
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of insulin like growth factor binding protein 5 reduces liver fibrosis in chronic cholangiopathy.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jun;1822(6):996-1003. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.02.022. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22434064
-
Insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS2) deficiency delays liver fibrosis associated with cholestatic injury.Dis Model Mech. 2019 Jul 16;12(7):dmm038810. doi: 10.1242/dmm.038810. Dis Model Mech. 2019. PMID: 31262748 Free PMC article.
-
Periostin promotes hepatic fibrosis in mice by modulating hepatic stellate cell activation via αv integrin interaction.J Gastroenterol. 2016 Dec;51(12):1161-1174. doi: 10.1007/s00535-016-1206-0. Epub 2016 Apr 4. J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27039906
-
Biological effects and regulation of IGFBP5 in breast cancer.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 25;13:983793. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.983793. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36093095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 relieves fibrosis through depolarizing of hepatic stellate cell in NASH.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Nov 29;13(11):1011. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05452-x. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36446766 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the mechanical microenvironment in cancer development and progression.Cancer Biol Med. 2020 May 15;17(2):282-292. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2019.0437. Cancer Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32587769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins-3 and -5: central mediators of fibrosis and promising new therapeutic targets.Open Rheumatol J. 2012;6:140-5. doi: 10.2174/1874312901206010140. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Open Rheumatol J. 2012. PMID: 22802912 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor system in cancer: novel targeted therapies.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:538019. doi: 10.1155/2015/538019. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25866791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical role of insulin‑like growth factor binding protein‑5 in methamphetamine‑induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Nov;10(5):2306-12. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2572. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 25230843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blomhoff R, Wake K. Perisinusoidal stellate cells of the liver: important roles in retinol metabolism and fibrosis 6. FASEB J. 1991;5:271–277. - PubMed
-
- Kinnman N, Hultcrantz R, Barbu V, Rey C, Wendum D, Poupon R, Housset C. PDGF-mediated chemoattraction of hepatic stellate cells by bile duct segments in cholestatic liver injury. Lab Invest. 2000;80:697–707. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

