BisoGenet: a new tool for gene network building, visualization and analysis
- PMID: 20163717
- PMCID: PMC3098113
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-91
BisoGenet: a new tool for gene network building, visualization and analysis
Abstract
Background: The increasing availability and diversity of omics data in the post-genomic era offers new perspectives in most areas of biomedical research. Graph-based biological networks models capture the topology of the functional relationships between molecular entities such as gene, protein and small compounds and provide a suitable framework for integrating and analyzing omics-data. The development of software tools capable of integrating data from different sources and to provide flexible methods to reconstruct, represent and analyze topological networks is an active field of research in bioinformatics.
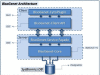
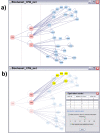
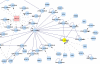
Results: BisoGenet is a multi-tier application for visualization and analysis of biomolecular relationships. The system consists of three tiers. In the data tier, an in-house database stores genomics information, protein-protein interactions, protein-DNA interactions, gene ontology and metabolic pathways. In the middle tier, a global network is created at server startup, representing the whole data on bioentities and their relationships retrieved from the database. The client tier is a Cytoscape plugin, which manages user input, communication with the Web Service, visualization and analysis of the resulting network.
Conclusion: BisoGenet is able to build and visualize biological networks in a fast and user-friendly manner. A feature of Bisogenet is the possibility to include coding relations to distinguish between genes and their products. This feature could be instrumental to achieve a finer grain representation of the bioentities and their relationships. The client application includes network analysis tools and interactive network expansion capabilities. In addition, an option is provided to allow other networks to be converted to BisoGenet. This feature facilitates the integration of our software with other tools available in the Cytoscape platform. BisoGenet is available at http://bio.cigb.edu.cu/bisogenet-cytoscape/.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GenePro: a Cytoscape plug-in for advanced visualization and analysis of interaction networks.Bioinformatics. 2006 Sep 1;22(17):2178-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl356. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16921162
-
Biana: a software framework for compiling biological interactions and analyzing networks.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Jan 27;11:56. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-56. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20105306 Free PMC article.
-
BioNetBuilder: automatic integration of biological networks.Bioinformatics. 2007 Feb 1;23(3):392-3. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl604. Epub 2006 Nov 30. Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17138585
-
Tools for visually exploring biological networks.Bioinformatics. 2007 Oct 15;23(20):2651-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm401. Epub 2007 Aug 25. Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17720984 Review.
-
Graphs in molecular biology.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Sep 27;8 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):S8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-S6-S8. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17903289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interactions of miR-323/miR-326/miR-329 and miR-130a/miR-155/miR-210 as prognostic indicators for clinical outcome of glioblastoma patients.J Transl Med. 2013 Jan 9;11:10. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-10. J Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23302469 Free PMC article.
-
Choline protects against cardiac hypertrophy induced by increased after-load.Int J Biol Sci. 2013;9(3):295-302. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.5976. Epub 2013 Mar 8. Int J Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23493786 Free PMC article.
-
SILGGM: An extensive R package for efficient statistical inference in large-scale gene networks.PLoS Comput Biol. 2018 Aug 13;14(8):e1006369. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006369. eCollection 2018 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2018. PMID: 30102702 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay Between Amphetamine and Activity Level in Gene Networks of the Mouse Striatum.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2018 Dec 11;12:1177932218815152. doi: 10.1177/1177932218815152. eCollection 2018. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2018. PMID: 30559594 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key regulatory genes connected to NF-κB family of proteins in visceral adipose tissues using gene expression and weighted protein interaction network.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 23;14(4):e0214337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214337. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31013288 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

