Interactions among HAMP domain repeats act as an osmosensing molecular switch in group III hybrid histidine kinases from fungi
- PMID: 20164185
- PMCID: PMC2852951
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.075721
Interactions among HAMP domain repeats act as an osmosensing molecular switch in group III hybrid histidine kinases from fungi
Abstract
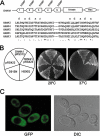
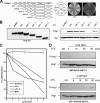
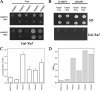
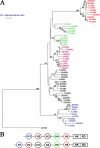
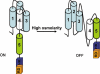
The members of group III hybrid histidine kinases (HHK) are ubiquitous in fungi. Group III HHK have been implicated to function as osmosensors in the high osmolarity glycerol (HOG) pathway that is essential for fungal survival under high osmolarity stress. Recent literature suggests that group III HHK are also involved in conidia formation, virulence in several filamentous fungi, and are an excellent molecular target for antifungal agents. Thus, group III HHK constitute a very important group of sensor kinases. Structurally, group III HHK are distinct from Sln1p, the osmosensing HHK that regulates the HOG pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Group III HHK lack any transmembrane domain and typically contain HAMP domain repeats at the N terminus. Until now, it is not clear how group III HHK function as an osmosensor to regulate the HOG pathway. To investigate this, we undertook molecular characterization of DhNIK1, an ortholog from osmotolerant yeast Debaryomyces hansenii. We show here that DhNIK1 could complement sln1 mutation in S. cerevisiae thereby confirming its role as a bona fide osmosensor. We further investigated the role of HAMP domains by deleting them systematically. Our results clearly indicate that the HAMP4 domain is crucial for osmosensing by DhNik1p. Most importantly, we also show that the alternative interaction among the HAMP domains regulates the activity of DhNik1p like an "on-off switch" and thus provides, for the first time, an insight into the molecular mechanism of osmosensing by this group of HHKs.
Figures


Comment in
-
Identifying divergent HAMP domains and poly-HAMP chains.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 4;285(23):le7; author reply 1e8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.L109.075721. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20511236 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Distinct role of HAMP and HAMP-like linker domains in regulating the activity of Hik1p, a hybrid histidine kinase 3 from Magnaporthe oryzae.Mol Genet Genomics. 2021 Sep;296(5):1135-1145. doi: 10.1007/s00438-021-01809-7. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Mol Genet Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34196769
-
Differential role of HAMP-like linkers in regulating the functionality of the group III histidine kinase DhNik1p.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 18;289(29):20245-58. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.554303. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24895133 Free PMC article.
-
The sixth HAMP domain negatively regulates the activity of the group III HHK containing seven HAMP domains.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Aug 16;438(1):140-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.07.041. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23876316
-
Hybrid histidine kinases in pathogenic fungi.Mol Microbiol. 2015 Mar;95(6):914-24. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12911. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Mol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25560420 Review.
-
Phenylpyrroles: 30 Years, Two Molecules and (Nearly) No Resistance.Front Microbiol. 2016 Dec 16;7:2014. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.02014. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 28018333 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The apical annuli of Toxoplasma gondii are composed of coiled-coil and signalling proteins embedded in the inner membrane complex sutures.Cell Microbiol. 2020 Jan;22(1):e13112. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13112. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Cell Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31470470 Free PMC article.
-
The N-terminus of the Aspergillus fumigatus group III hybrid histidine kinase TcsC is essential for its physiological activity and targets the protein to the nucleus.mBio. 2024 Jul 17;15(7):e0118424. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01184-24. Epub 2024 Jun 4. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38832777 Free PMC article.
-
Osmosensing and osmoregulation in unicellular eukaryotes.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Mar;31(3):435-43. doi: 10.1007/s11274-015-1811-8. Epub 2015 Feb 1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25638456 Review.
-
Distinct role of HAMP and HAMP-like linker domains in regulating the activity of Hik1p, a hybrid histidine kinase 3 from Magnaporthe oryzae.Mol Genet Genomics. 2021 Sep;296(5):1135-1145. doi: 10.1007/s00438-021-01809-7. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Mol Genet Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34196769
-
Differential role of HAMP-like linkers in regulating the functionality of the group III histidine kinase DhNik1p.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 18;289(29):20245-58. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.554303. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24895133 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Santos J. L., Shiozaki K. (2001) Sci. STKE 2001, RE1. - PubMed
-
- Nemecek J. C., Wüthrich M., Klein B. S. (2006) Science 312, 583–588 - PubMed
-
- Viaud M., Fillinger S., Liu W., Polepalli J. S., Le Pêcheur P., Kunduru A. R., Leroux P., Legendre L. (2006) Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 19, 1042–1050 - PubMed
-
- Bahn Y. S., Xue C., Idnurm A., Rutherford J. C., Heitman J., Cardenas M. E. (2007) Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 5, 57–69 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

