The phospholipid-binding protein SESTD1 is a novel regulator of the transient receptor potential channels TRPC4 and TRPC5
- PMID: 20164195
- PMCID: PMC2852980
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.068304
The phospholipid-binding protein SESTD1 is a novel regulator of the transient receptor potential channels TRPC4 and TRPC5
Abstract
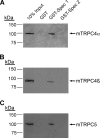
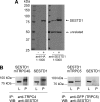
TRPC4 and TRPC5 are two closely related members of the mammalian transient receptor potential cation channel family that have been implicated in important physiological functions, such as growth cone guidance and smooth muscle contraction. To further unravel the role of TRPC4 and TRPC5 in these processes in vivo, detailed information about the molecular composition of native channel complexes and their association with cellular signaling networks is needed. We therefore searched a human aortic cDNA library for novel TRPC4-interacting proteins using a modified yeast two-hybrid assay. This screen identified SESTD1, a previously uncharacterized protein containing a lipid-binding SEC14-like domain as well as spectrin-type cytoskeleton interaction domains. SESTD1 was found to associate with TRPC4 and TRPC5 via the channel's calmodulin- and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-binding domain. In functional studies, we demonstrate that SESTD1 binds several phospholipid species in vitro and is essential for efficient receptor-mediated activation of TRPC5. Notably, phospholipid binding to SESTD1 was Ca(2+)-dependent. Because TRPC4 and -5 conduct Ca(2+), SESTD1-channel signaling may be bidirectional and also couple TRPC activity to lipid signaling through SESTD1. The modulation of TRPC channel function by specific lipid-binding proteins, such as SESTD1, adds another facet to the complex regulation of these channels complementary to the previously described effects of direct channel-phospholipid interaction.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Trans-activation response (TAR) RNA-binding protein 2 is a novel modulator of transient receptor potential canonical 4 (TRPC4) protein.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 4;289(14):9766-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.557066. Epub 2014 Feb 21. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24563462 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Gαi subunits as novel direct activators of transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC)4 and TRPC5 channels.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 18;287(21):17029-17039. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.326553. Epub 2012 Mar 28. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22457348 Free PMC article.
-
TRPC4- and TRPC4-containing channels.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:85-128. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_5. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24756704 Review.
-
TRPC5.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:129-56. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_6. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24756705 Review.
-
Junctate, an inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor associated protein, is present in rodent sperm and binds TRPC2 and TRPC5 but not TRPC1 channels.Dev Biol. 2005 Oct 1;286(1):326-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.08.006. Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 16153633
Cited by
-
Human MicroRNA miR-532-5p Exhibits Antiviral Activity against West Nile Virus via Suppression of Host Genes SESTD1 and TAB3 Required for Virus Replication.J Virol. 2015 Dec 16;90(5):2388-402. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02608-15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26676784 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a membrane-targeting domain of the transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC)4 channel unrelated to its formation of a tetrameric structure.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 12;289(50):34990-5002. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.584649. Epub 2014 Oct 27. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25349210 Free PMC article.
-
The phospholipid-binding protein SESTD1 negatively regulates dendritic spine density by interfering with Rac1-Trio8 signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2015 Aug 14;5:13250. doi: 10.1038/srep13250. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26272757 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Studies for Body Conformation Traits in Korean Holstein Population.Animals (Basel). 2023 Sep 19;13(18):2964. doi: 10.3390/ani13182964. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760364 Free PMC article.
-
Electron cryo-microscopy structure of the canonical TRPC4 ion channel.Elife. 2018 May 2;7:e36615. doi: 10.7554/eLife.36615. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29717981 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

