Recruitment of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP0 to the virus particle
- PMID: 20164220
- PMCID: PMC2863764
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00126-10
Recruitment of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP0 to the virus particle
Abstract
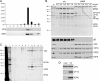
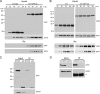
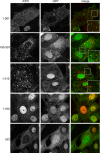
Although the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) tegument is comprised of a large number of viral and cellular proteins, how and where in the cell these proteins are recruited into the virus structure is poorly understood. We have shown previously that the immediate-early gene product ICP0 is packaged by a mechanism dependent on the major tegument protein VP22, while others have shown a requirement for ICP27. We now extend our studies to show that ICP0 packaging correlates directly with the ability of ICP0 to complex with VP22 in infected cells. ICP27 is not, however, present in this VP22-ICP0 complex but is packaged into the virion in a VP22- and ICP0-independent manner. Biochemical fractionation of virions indicated that ICP0 associates tightly with the virus capsid, but intranuclear capsids contained no detectable ICP0. The RING finger domain of ICP0 and the N terminus of VP22 were both shown to be essential but not sufficient for ICP0 packaging and complex formation. Strikingly, however, the N-terminal region of VP22, while unable to form a complex with ICP0, inhibited its translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. PML degradation by ICP0 was efficient in cells infected with this VP22 mutant virus, confirming that ICP0 retains activity. Hence, we would suggest that VP22 is an important molecular partner of ICP0 that controls at least one of its activities: its assembly into the virion. Moreover, we propose that the pathway by which VP22 recruits ICP0 to the virion may begin in the nucleus prior to ICP0 translocation to its final site of assembly in the cytoplasm.
Figures
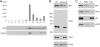




Similar articles
-
A pre-immediate-early role for tegument ICP0 in the proteasome-dependent entry of herpes simplex virus.J Virol. 2011 Jun;85(12):5910-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00267-11. Epub 2011 Apr 6. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21471243 Free PMC article.
-
A network of protein interactions around the herpes simplex virus tegument protein VP22.J Virol. 2012 Dec;86(23):12971-82. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01913-12. Epub 2012 Sep 19. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22993164 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of the herpes simplex virus VP22-encoding gene (UL49) alters the expression, localization, and virion incorporation of ICP0.J Virol. 2005 Aug;79(15):9735-45. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.15.9735-9745.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16014935 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the herpes simplex virus tegument protein VP22 has no effect on incorporation of VP22 into the virus but is involved in optimal expression and virion packaging of ICP0.J Virol. 2005 Nov;79(22):14057-68. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.22.14057-14068.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16254340 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP27 is required for efficient incorporation of ICP0 and ICP4 into virions.J Virol. 2008 Jan;82(1):268-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01588-07. Epub 2007 Oct 24. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 17959681 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A pre-immediate-early role for tegument ICP0 in the proteasome-dependent entry of herpes simplex virus.J Virol. 2011 Jun;85(12):5910-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00267-11. Epub 2011 Apr 6. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21471243 Free PMC article.
-
ICP0 dismantles microtubule networks in herpes simplex virus-infected cells.PLoS One. 2010 Jun 8;5(6):e10975. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010975. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20544015 Free PMC article.
-
The precise function of alphaherpesvirus tegument proteins and their interactions during the viral life cycle.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 2;15:1431672. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1431672. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39015737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a novel neurovirulence factor encoded by the cryptic orphan gene UL31.6 of herpes simplex virus 1.J Virol. 2024 Jul 23;98(7):e0074724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00747-24. Epub 2024 May 31. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38819171 Free PMC article.
-
HSV-1 ICP27 targets the TBK1-activated STING signalsome to inhibit virus-induced type I IFN expression.EMBO J. 2016 Jul 1;35(13):1385-99. doi: 10.15252/embj.201593458. Epub 2016 May 27. EMBO J. 2016. PMID: 27234299 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

