Development of an intergenotypic hepatitis C virus (HCV) cell culture method to assess antiviral susceptibilities and resistance development of HCV NS3 protease genes from HCV genotypes 1 to 6
- PMID: 20164226
- PMCID: PMC2863784
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02698-09
Development of an intergenotypic hepatitis C virus (HCV) cell culture method to assess antiviral susceptibilities and resistance development of HCV NS3 protease genes from HCV genotypes 1 to 6
Abstract
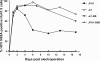
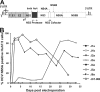
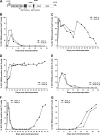
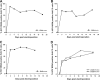
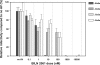
Protease inhibitors (PIs) of hepatitis C virus (HCV) provide an additional or alternative therapy for chronic infection. However, assessment of their efficacy and ability to inhibit replication of different genotypes is hampered by the lack of a convenient animal model or a method for in vitro culture of HCV other than the type 1/2-based replicons and the infectious genotype 2a clone JFH1. To address this problem, we constructed a panel of replication-competent chimeric Jc1 (pFK JFH1/J6/C-846) clones containing protease and NS4A coding sequences from all six major genotypes, enabling the determination of replication and the susceptibility to PIs. Chimeras showed substantial variability in replication kinetics, attributable in part to naturally occurring polymorphisms and differing requirements for adaptive mutations in NS3 and NS4A. Through calculation of 50% inhibitory concentrations (IC(50)s) of BILN 2061, measuring reduction in the number of focus-forming units/ml (FFU/ml) and replication inhibition, consistent genotype-associated differences in antiviral susceptibilities were observed. IC(50)s for genotype 1b, 4a, and 6a-derived chimeras (1 to 3 nM) were approximately 100-fold lower than those for genotypes 2a, 3a, and 5a (range, 80 to 720 nM), implying major differences in response to therapy. In vitro passage in increasing concentrations of BILN 2061 rapidly induced resistance-associated mutations at position 168 in chimeras of all 6 genotypes and at position 156 in genotypes 1b and 4a, each with substantial variability in the identity of substituted amino acids. The system will allow future comprehensive phenotypic characterization of naturally occurring and treatment-induced mutations for PIs in trial or entering clinical use.
Figures

References
-
- Anonymous. 1999. Global surveillance and control of hepatitis C. Report of a WHO Consultation organized in collaboration with the Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board, Antwerp, Belgium. J. Viral Hepat. 6:35-47. - PubMed
-
- Binder, J., S. Tetangco, M. Wick, K. Maegley, L. Lingardo, A. Patick, and G. Smith. 2007. Development of hepatitis C virus (HCV) chimeric replicons for identifying broad spectrum NS3 protease inhibitors. Antiviral Res. 74:A38. - PubMed
-
- Bukh, J. 1995. Genetic heterogeneity of hepatitis C virus: quasispecies and genotypes. Semin. Liver Dis. 15:41-63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

