Herpes simplex virus 1 regulatory protein ICP27 undergoes a head-to-tail intramolecular interaction
- PMID: 20164236
- PMCID: PMC2863791
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02319-09
Herpes simplex virus 1 regulatory protein ICP27 undergoes a head-to-tail intramolecular interaction
Abstract
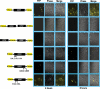
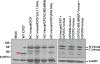
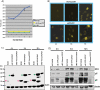
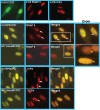
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) regulatory protein ICP27 is a multifunction functional protein that interacts with many cellular proteins. A number of the proteins with which ICP27 interacts require that both the N and C termini of ICP27 are intact. These include RNA polymerase II, TAP/NXF1, and Hsc70. We tested the possibility that the N and C termini of ICP27 could undergo a head-to-tail intramolecular interaction that exists in open and closed configurations for different binding partners. Here, we show by bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) by acceptor photobleaching that ICP27 undergoes a head-to-tail intramolecular interaction but not head-to-tail or tail-to-tail intermolecular interactions. Substitution mutations in the N or C termini showed that the leucine-rich region (LRR) in the N terminus and the zinc finger-like region in the C terminus must be intact for intramolecular interactions. A recombinant virus, vNC-Venus-ICP27, was constructed, and this virus was severely impaired for virus replication. The expression of NC-Venus-ICP27 protein was delayed compared to ICP27 expression in wild-type HSV-1 infection, but NC-Venus-ICP27 was abundantly expressed at late times of infection. Because the renaturation of the Venus fluorescent protein results in a covalent bonding of the two halves of the Venus molecule, the head-to-tail interaction of NC-Venus-ICP27 locks ICP27 in a closed configuration. We suggest that the population of locked ICP27 molecules is not able to undergo further protein-protein interactions.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Head-to-tail intramolecular interaction of herpes simplex virus type 1 regulatory protein ICP27 is important for its interaction with cellular mRNA export receptor TAP/NXF1.mBio. 2010 Nov 9;1(5):e00268-10. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00268-10. mBio. 2010. PMID: 21060739 Free PMC article.
-
The cellular RNA export receptor TAP/NXF1 is required for ICP27-mediated export of herpes simplex virus 1 RNA, but the TREX complex adaptor protein Aly/REF appears to be dispensable.J Virol. 2009 Jul;83(13):6335-46. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00375-09. Epub 2009 Apr 15. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19369354 Free PMC article.
-
Three arginine residues within the RGG box are crucial for ICP27 binding to herpes simplex virus 1 GC-rich sequences and for efficient viral RNA export.J Virol. 2010 Jul;84(13):6367-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00509-10. Epub 2010 Apr 21. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20410270 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of an HSV-1 regulatory protein that appears to impair host cell splicing.Infect Agents Dis. 1994 Apr-Jun;3(2-3):59-67. Infect Agents Dis. 1994. PMID: 7812656 Review.
-
The many roles of the regulatory protein ICP27 during herpes simplex virus infection.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:5241-56. doi: 10.2741/3078. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18508584 Review.
Cited by
-
The interaction of the cellular export adaptor protein Aly/REF with ICP27 contributes to the efficiency of herpes simplex virus 1 mRNA export.J Virol. 2013 Jul;87(13):7210-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00738-13. Epub 2013 May 1. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23637401 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase and fusion glycoproteins of human parainfluenza virus type III regulates viral growth in vivo.mBio. 2013 Oct 22;4(5):e00803-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00803-13. mBio. 2013. PMID: 24149514 Free PMC article.
-
Head-to-tail intramolecular interaction of herpes simplex virus type 1 regulatory protein ICP27 is important for its interaction with cellular mRNA export receptor TAP/NXF1.mBio. 2010 Nov 9;1(5):e00268-10. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00268-10. mBio. 2010. PMID: 21060739 Free PMC article.
-
The Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus ORF57 Protein and Its Multiple Roles in mRNA Biogenesis.Front Microbiol. 2012 Feb 20;3:59. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00059. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22363332 Free PMC article.
-
The HSV-1 Transcription Factor ICP4 Confers Liquid-Like Properties to Viral Replication Compartments.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 24;22(9):4447. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094447. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33923223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachi, A., I. C. Braun, J. P. Rodrigues, N. Pante, K. Ribbeck, C. von Kobbe, U. Kutay, M. Wilm, D. Gorlich, M. Carmo-Fonseca, and E. Izaurralde. 2000. The C-terminal domain of TAP interacts with the nuclear pore complex and promotes export of specific CTE-bearing RNA substrates. RNA 6:136-158. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

