Tight junction-associated MARVEL proteins marveld3, tricellulin, and occludin have distinct but overlapping functions
- PMID: 20164257
- PMCID: PMC2847524
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-08-0734
Tight junction-associated MARVEL proteins marveld3, tricellulin, and occludin have distinct but overlapping functions
Abstract
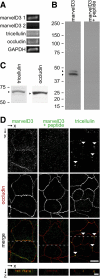
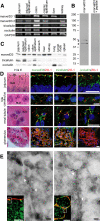
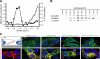
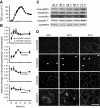
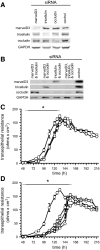
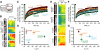
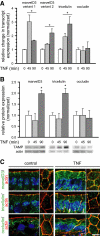
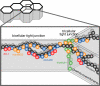
In vitro studies have demonstrated that occludin and tricellulin are important for tight junction barrier function, but in vivo data suggest that loss of these proteins can be overcome. The presence of a heretofore unknown, yet related, protein could explain these observations. Here, we report marvelD3, a novel tight junction protein that, like occludin and tricellulin, contains a conserved four-transmembrane MARVEL (MAL and related proteins for vesicle trafficking and membrane link) domain. Phylogenetic tree reconstruction; analysis of RNA and protein tissue distribution; immunofluorescent and electron microscopic examination of subcellular localization; characterization of intracellular trafficking, protein interactions, dynamic behavior, and siRNA knockdown effects; and description of remodeling after in vivo immune activation show that marvelD3, occludin, and tricellulin have distinct but overlapping functions at the tight junction. Although marvelD3 is able to partially compensate for occludin or tricellulin loss, it cannot fully restore function. We conclude that marvelD3, occludin, and tricellulin define the tight junction-associated MARVEL protein family. The data further suggest that these proteins are best considered as a group with both redundant and unique contributions to epithelial function and tight junction regulation.
Figures


References
-
- Abascal F., Zardoya R., Posada D. ProtTest: selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:2104–2105. - PubMed
-
- Abramoff M. D., Magelhaes P. J., Ram S. J. Image processing with Image. J. Biophoton. Int. 2004;11:36–42.
-
- Balda M. S., Whitney J. A., Flores C., Gonzalez S., Cereijido M., Matter K. Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. J. Cell Biol. 1996;134:1031–1049. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Breitwieser G. E., McLenithan J. C., Cortese J. F., Shields J. M., Oliva M. M., Majewski J. L., Machamer C. E., Yang V. W. Colonic epithelium-enriched protein A4 is a proteolipid that exhibits ion channel characteristics. Am. J. Physiol. 1997;272:C957–C965. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

