Characterization of the Ebola virus nucleoprotein-RNA complex
- PMID: 20164259
- PMCID: PMC2878588
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.019794-0
Characterization of the Ebola virus nucleoprotein-RNA complex
Abstract
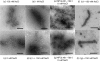
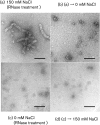
When Ebola virus nucleoprotein (NP) is expressed in mammalian cells, it assembles into helical structures. Here, the recombinant NP helix purified from cells expressing NP was characterized biochemically and morphologically. We found that the recombinant NP helix is associated with non-viral RNA, which is not protected from RNase digestion and that the morphology of the helix changes depending on the environmental salt concentration. The N-terminal 450 aa residues of NP are sufficient for these properties. However, digestion of the NP-associated RNA eliminates the plasticity of the helix, suggesting that this RNA is an essential structural component of the helix, binding to individual NP molecules via the N-terminal 450 aa. These findings enhance our knowledge of Ebola virus assembly and understanding of the Ebola virus life cycle.
Figures

References
-
- Albertini, A. A., Wernimont, A. K., Muziol, T., Ravelli, R. B., Clapier, C. R., Schoehn, G., Weissenhorn, W. & Ruigrok, R. W. (2006). Crystal structure of the rabies virus nucleoprotein-RNA complex. Science 313, 360–363. - PubMed
-
- Bhella, D., Ralph, A., Murphy, L. B. & Yeo, R. P. (2002). Significant differences in nucleocapsid morphology within the Paramyxoviridae. J Gen Virol 83, 1831–1839. - PubMed
-
- Errington, W. & Emmerson, P. T. (1997). Assembly of recombinant Newcastle disease virus nucleocapsid protein into nucleocapsid-like structures is inhibited by the phosphoprotein. J Gen Virol 78, 2335–2339. - PubMed
-
- Fooks, A. R., Schadeck, E., Liebert, U. G., Dowsett, A. B., Rima, B. K., Steward, M., Stephenson, J. R. & Wilkinson, G. W. (1995). High-level expression of the measles virus nucleocapsid protein by using a replication-deficient adenovirus vector: induction of an MHC-1-restricted CTL response and protection in a murine model. Virology 210, 456–465. - PubMed
-
- Green, T. J., Zhang, X., Wertz, G. W. & Luo, M. (2006). Structure of the vesicular stomatitis virus nucleoprotein-RNA complex. Science 313, 357–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

