Butrin, isobutrin, and butein from medicinal plant Butea monosperma selectively inhibit nuclear factor-kappaB in activated human mast cells: suppression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-8
- PMID: 20164300
- PMCID: PMC2872957
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.109.165209
Butrin, isobutrin, and butein from medicinal plant Butea monosperma selectively inhibit nuclear factor-kappaB in activated human mast cells: suppression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-8
Abstract
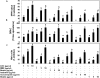
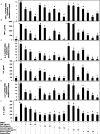
Activation of mast cells in rheumatoid synovial tissue has often been associated with tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-8 production and disease pathogenesis by adjacent cell types. Butea monosperma (BM) is a well known medicinal plant in India and the tropics. The aim of this study was to examine whether a standardized extract of BM flower (BME) could inhibit inflammatory reactions in human mast cells (HMC) using activated HMC-1 cells as a model. Four previously characterized polyphenols--butrin, isobutrin, isocoreopsin, and butein--were isolated from BME by preparative thin layer chromatography, and their purity and molecular weights were determined by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis. Our results showed that butrin, isobutrin, and butein significantly reduced the phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and calcium ionophore A23187-induced inflammatory gene expression and production of TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-8 in HMC-1 cells by inhibiting the activation of NF-kappaB. In addition, isobutrin was most potent in suppressing the NF-kappaB p65 activation by inhibiting IkappaBalpha degradation, whereas butrin and butein were relatively less effective. In vitro kinase activity assay revealed that isobutrin was a potent inhibitor of IkappaB kinase complex activity. This is the first report identifying the molecular basis of the reported anti-inflammatory effects of BME and its constituents butrin, isobutrin, and butein. The novel pharmacological actions of these polyphenolic compounds indicate potential therapeutic value for the treatment of inflammatory and other diseases in which activated mast cells play a role.
Figures


References
-
- Arend WP, Dayer JM. (1995) Inhibition of the production and effects of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38:151–160 - PubMed
-
- Azzolina A, Bongiovanni A, Lampiasi N. (2003) Substance P induces TNF-alpha and IL-6 production through NF kappa B in peritoneal mast cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1643:75–83 - PubMed
-
- Bandara BMR, Kumar NS, Wimalasiri KMS. (1990) Constituents of the stem bark from Butea monosperma. J Natl Sci Counc Sri Lanka 18:97–103
-
- Bhargava SK. (1986) Estrogenic and postcoital anticonceptive activity in rats of butin isolated from Butea monosperma seed. J Ethnopharmacology 18:95–101 - PubMed
-
- Blois MS. (1958) Antioxidant determination by the use of a stable free radical. Nature 181:1199–1200
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

