Reversal of prolonged dopamine inhibition of dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area
- PMID: 20164301
- PMCID: PMC2872954
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.109.163931
Reversal of prolonged dopamine inhibition of dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area
Abstract
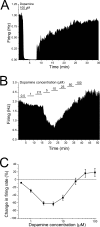
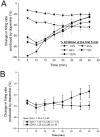
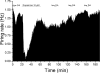
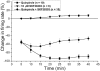
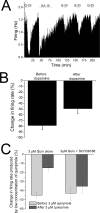
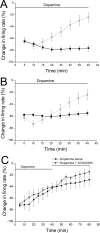
Drug abuse-induced plasticity of putative dopaminergic (pDAergic) ventral tegmental area (VTA) neurons may play an important role in changes in the mesocorticolimbic system that lead to the development of addiction. In the present study, extracellular recordings were used to examine time-dependent effects of dopamine (DA) on pDAergic VTA neurons in rat brain slices. Administration of DA (2.5-10 microM) for 40 min resulted in inhibition followed by partial or full reversal of that inhibition. The reduced sensitivity to DA inhibition lasted 30 to 90 min after washout of the long-term dopamine administration. The inhibition reversal was not observed with 40-min administration of the D2 agonist quinpirole (25-200 nM), so this phenomenon was not the result of desensitization induced solely by stimulation of D2 DA receptors. Inhibition reversal could be observed with the coapplication of quinpirole and the D1/D5 agonist SKF38393 [(+/-)-1-phenyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-(1H)-3-benzazepine-7,8-diol hydrobromide], suggesting a D1/D5 mechanism for the reversal. Furthermore, D1/D5 antagonists, given in the presence of prolonged DA exposure, prevented the inhibition reversal. Application of 3 microM quinpirole caused desensitization to low quinpirole concentrations that was blocked by a D1/D5 antagonist. These data suggest that coactivation of D1/D5 receptors and D2 receptors in the VTA results in desensitization of autoinhibitory D2 receptors. Prolonged increases in pDAergic tone in the VTA that may occur in vivo with drugs of abuse could reduce the regulation of firing by D2 dopamine receptor activation, producing long-term alteration in information processing related to reward and reinforcement.
Figures
References
-
- Barton AC, Black LE, Sibley DR. (1991) Agonist-induced desensitization of D2 dopamine receptors in human Y-79 retinoblastoma cells. Mol Pharmacol 39:650–658 - PubMed
-
- Brodie MS, Dunwiddie TV. (1987) Cholecystokinin potentiates dopamine inhibition of mesencephalic dopamine neurons in vitro. Brain Res 425:106–113 - PubMed
-
- Brodie MS, Dunwiddie TV. (1990) Cocaine effects in the ventral tegmental area: Evidence for an indirect dopaminergic mechanism of action. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 342:660–665 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

