Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates hedonic feeding by acting on the mesolimbic dopamine system
- PMID: 20164338
- PMCID: PMC2846779
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5768-09.2010
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates hedonic feeding by acting on the mesolimbic dopamine system
Abstract
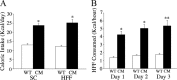
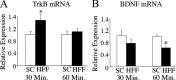
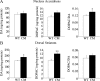
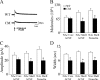
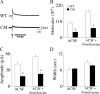
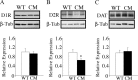
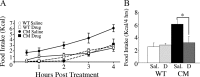
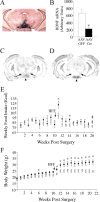
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its receptor, TrkB, play prominent roles in food intake regulation through central mechanisms. However, the neural circuits underlying their anorexigenic effects remain largely unknown. We showed previously that selective BDNF depletion in the ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) of mice resulted in hyperphagic behavior and obesity. Here, we sought to ascertain whether its regulatory effects involved the mesolimbic dopamine system, which mediates motivated and reward-seeking behaviors including consumption of palatable food. We found that expression of BDNF and TrkB mRNA in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) of wild-type mice was influenced by consumption of palatable, high-fat food (HFF). Moreover, amperometric recordings in brain slices of mice depleted of central BDNF uncovered marked deficits in evoked release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) shell and dorsal striatum but normal secretion in the NAc core. Mutant mice also exhibited dramatic increases in HFF consumption, which were exacerbated when access to HFF was restricted. However, mutants displayed enhanced responses to D(1) receptor agonist administration, which normalized their intake of HFF in a 4 h food intake test. Finally, in contrast to deletion of Bdnf in the VMH of mice, which resulted in increased intake of standard chow, BDNF depletion in the VTA elicited excessive intake of HFF but not of standard chow and increased body weights under HFF conditions. Our findings indicate that the effects of BDNF on eating behavior are neural substrate-dependent and that BDNF influences hedonic feeding via positive modulation of the mesolimbic dopamine system.
Figures
References
-
- Abizaid A, Liu ZW, Andrews ZB, Shanabrough M, Borok E, Elsworth JD, Roth RH, Sleeman MW, Picciotto MR, Tschöp MH, Gao XB, Horvath TL. Ghrelin modulates the activity and synaptic input organization of midbrain dopamine neurons while promoting appetite. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:3229–3239. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baldo BA, Alsene KM, Negron A, Kelley AE. Hyperphagia induced by GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition of the nucleus accumbens shell: dependence on intact neural output from the central amygdaloid region. Behav Neurosci. 2005;119:1195–1206. - PubMed
-
- Bariohay B, Lebrun B, Moyse E, Jean A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor plays a role as an anorexigenic factor in the dorsal vagal complex. Endocrinology. 2005;146:5612–5620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
