Response of adult mouse uterus to early disruption of estrogen receptor-alpha signaling is influenced by Krüppel-like factor 9
- PMID: 20164373
- PMCID: PMC2972657
- DOI: 10.1677/JOE-09-0474
Response of adult mouse uterus to early disruption of estrogen receptor-alpha signaling is influenced by Krüppel-like factor 9
Abstract
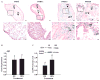
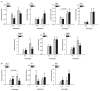
Inappropriate early exposure of the hormone-responsive uterus to estrogenic compounds is associated with increased risk for adult reproductive diseases including endometrial cancers. While the dysregulation of estrogen receptor-alpha (ESR1) signaling is well acknowledged to mediate early events in tumor initiation, mechanisms contributing to sustained ESR1 activity later in life and leading to induction of oncogenic pathways remain poorly understood. We had shown previously that the transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 9 (KLF9) represses ESR1 expression and activity in Ishikawa endometrial glandular epithelial cells. We hypothesized that KLF9 functions as a tumor suppressor, and that loss of its expression enhances ESR1 signaling. Here, we evaluated the contribution of KLF9 to early perturbations in uterine ESR1 signaling pathways elicited by the administration of synthetic estrogen diethylstilbestrol (DES) to wild-type (WT) and Klf9 null (KO) mice on postnatal days (PNDs) 1-5. Uterine tissues collected at PND84 were subjected to histological, immunological, and molecular analyses. Compared with WT mice, KO mice demonstrated larger endometrial glands and lower endometrial gland numbers; DES exposure exacerbated these differences. Loss of KLF9 expression resulted in increased glandular ESR1 immunoreactivity with DES, without effects on serum estradiol levels. Quantitative RT-PCR analyses indicated altered expression of uterine genes commonly dysregulated in endometrial cancers (Akt1, Mmp9, Slpi, and Tgfbeta1) and of those involved in growth regulation (Fos, Myc, Tert, and Syk), with loss of Klf9, alone or in concert with DES. Our data support a molecular network between KLF9 and ESR1 in the uterus, and suggest that silencing of KLF9 may contribute to endometrial dysfunctions initiated by aberrant estrogen action.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




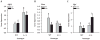
Similar articles
-
Nuclear receptor co-regulator Krüppel-like factor 9 and prohibitin 2 expression in estrogen-induced epithelial cell proliferation in the mouse uterus.J Endocrinol. 2009 Jan;200(1):63-73. doi: 10.1677/JOE-08-0383. Epub 2008 Oct 3. J Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 18835980 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-like factor 9 loss-of-expression in human endometrial carcinoma links altered expression of growth-regulatory genes with aberrant proliferative response to estrogen.Biol Reprod. 2011 Aug;85(2):378-85. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.090654. Epub 2011 May 4. Biol Reprod. 2011. PMID: 21543766 Free PMC article.
-
Kruppel-like factor 9 is a negative regulator of ligand-dependent estrogen receptor alpha signaling in Ishikawa endometrial adenocarcinoma cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2007 Dec;21(12):2988-3001. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0242. Epub 2007 Aug 23. Mol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17717078
-
The emerging role of Krüppel-like factors in endocrine-responsive cancers of female reproductive tissues.J Endocrinol. 2010 Mar;204(3):223-31. doi: 10.1677/JOE-09-0329. Epub 2009 Oct 15. J Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 19833720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Krüppel-like factors in female reproductive system pathologies.J Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Apr;54(2):R89-R101. doi: 10.1530/JME-14-0310. Epub 2015 Feb 5. J Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25654975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Krüppel-like Factor-9 and Krüppel-like Factor-13: Highly Related, Multi-Functional, Transcriptional Repressors and Activators of Oncogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 30;15(23):5667. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235667. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A coregulatory network of NR2F1 and microRNA-140.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 3;8(12):e83358. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083358. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349493 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-like Factor 9 (KLF9) Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)-Promoting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Mice Fed High-Fat Diet.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 29;14(7):1737. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071737. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406507 Free PMC article.
-
The reproductive phenotype of mice null for transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 13 suggests compensatory function of family member Krüppel-like factor 9 in the peri-implantation uterus.Biol Reprod. 2012 Nov 16;87(5):115. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.112.102251. Print 2012 Nov. Biol Reprod. 2012. PMID: 22993382 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-like factor 9 (KLF9) prevents colorectal cancer through inhibition of interferon-related signaling.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Sep;36(9):946-55. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv104. Epub 2015 Jul 25. Carcinogenesis. 2015. PMID: 26210742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altomare DA, Testa JR. Perturbations of the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24:7455–7464. - PubMed
-
- Boggess JF, Zhou C, Bee-Jump VL, Gehrig PA, Whang YE. Estrogen receptor-dependent regulation of telomerase activity in human endometrial cancer cell lines. Gynecol Oncol. 2006;103:417–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

