The contribution of AKAP5 in amylase secretion from mouse parotid acini
- PMID: 20164376
- PMCID: PMC2867378
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00382.2009
The contribution of AKAP5 in amylase secretion from mouse parotid acini
Abstract
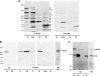
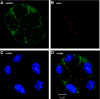
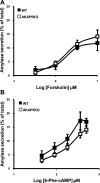
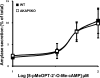
A-kinase (PKA) anchoring proteins (AKAPs) are essential for targeting type II PKA to specific locales in the cell to control function. In the present study, AKAP5 (formerly AKAP150) and AKAP6 were identified in mouse parotid acini by type II PKA regulatory subunit (RII) overlay assay and Western blot analysis of mouse parotid cellular fractions, and the role of AKAP5 in mouse parotid acinar cell secretion was determined. Mice were euthanized with CO(2). Immunofluorescence staining of acinar cells localized AKAP5 to the basolateral membrane, whereas AKAP6 was associated with the perinuclear region. In functional studies, amylase secretion from acinar cells of AKAP5 mutant [knockout (KO)] mice treated with the beta-adrenergic agonist, isoproterenol, was reduced overall by 30-40% compared with wild-type (WT) mice. In contrast, amylase secretion in response to the adenylyl cyclase (AC) activator, forskolin, and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) activator, N(6)-phenyl-cAMP, was not statistically different in acini from WT and AKAP5 KO mice. Treatment of acini with isoproterenol mimicked the effect of the Epac activator, 8-(4-methoxyphenylthio)-2'-O-methyladenosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (8-pMeOPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP), in stimulating Rap1. However, in contrast to isoproterenol, treatment of acini with 8-pMeOPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP resulted in stimulation of amylase secretion from both AKAP5 KO and WT acinar cells. As a scaffolding protein, AKAP5 was found to coimmunoprecipitate with AC6, but not AC8. Data suggest that isoproterenol-stimulated amylase secretion occurs via both an AKAP5/AC6/PKA complex and a PKA-independent, Epac pathway in mouse parotid acini.
Figures



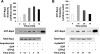
References
-
- Baggaley E, McLarnon S, Demeter I, Varga G, Bruce JI. Differential regulation of the apical plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPase by protein kinase A in parotid acinar cells. J Biol Chem 282: 37678–37693, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Bernfeld P. Enzymes of starch degradation and synthesis. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem 12: 379–428, 1951 - PubMed
-
- Bi Y, Williams JA. A role for Rho and Rac in secretagogue-induced amylase release by pancreatic acini. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 289: C22–C32, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

