Influence of the extracellular matrix and integrins on volume-sensitive osmolyte anion channels in C2C12 myoblasts
- PMID: 20164377
- PMCID: PMC2867394
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00359.2009
Influence of the extracellular matrix and integrins on volume-sensitive osmolyte anion channels in C2C12 myoblasts
Abstract
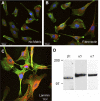
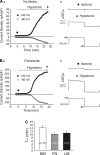
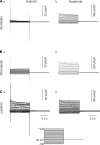
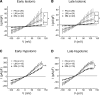
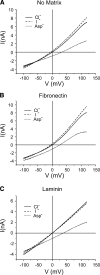
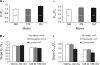
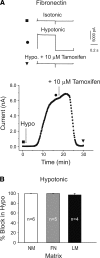
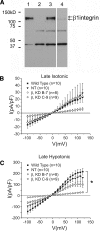
The purpose of this study was to determine whether extracellular matrix (ECM) composition through integrin receptors modulated the volume-sensitive osmolyte anion channels (VSOACs) in skeletal muscle-derived C2C12 cells. Cl(-) currents were recorded in whole cell voltage-clamped cells grown on laminin (LM), fibronectin (FN), or in the absence of a defined ECM (NM). Basal membrane currents recorded in isotonic media (300 mosmol/kg) were larger in cells grown on FN (3.8-fold at +100 mV) or LM (8.8-fold at +100 mV) when compared with NM. VSOAC currents activated by cell exposure to hypotonic solution were larger in cells grown on LM (1.72-fold at +100 mV) or FN (1.75-fold at +100 mV) compared with NM. Additionally, the kinetics of VSOAC activation was approximately 27% quicker on FN and LM. These currents were tamoxifen sensitive, displayed outward rectification, reversed at the equilibrium potential of Cl(-) and inactivated at potentials >+60 mV. Specific knockdown of beta(1)-integrin by short hairpin RNA interference strongly inhibited the VSOAC Cl(-) currents in cells plated on FN. In conclusion, ECM composition and integrins profoundly influence the biophysical properties and mechanisms of onset of VSOACs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Altered properties of volume-sensitive osmolyte and anion channels (VSOACs) and membrane protein expression in cardiac and smooth muscle myocytes from Clcn3-/- mice.J Physiol. 2004 Jun 1;557(Pt 2):439-56. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.059261. Epub 2004 Mar 12. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15020697 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal expression of sodium/bicarbonate cotransporter NBCn1 (SLC4A7) and its response to chronic metabolic acidosis.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 May;298(5):C1018-28. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00492.2009. Epub 2010 Feb 10. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20147654 Free PMC article.
-
Volume-activated chloride channels in rat parotid acinar cells.J Physiol. 1995 May 1;484 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):677-87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020695. J Physiol. 1995. PMID: 7623284 Free PMC article.
-
Chloride current activated by hypotonicity in cultured human astrocytoma cells.Exp Physiol. 1995 May;80(3):373-89. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1995.sp003854. Exp Physiol. 1995. PMID: 7543762
-
The ins and outs of fibronectin matrix assembly.J Cell Sci. 2003 Aug 15;116(Pt 16):3269-76. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00670. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12857786 Review.
Cited by
-
The LRRC8/VRAC anion channel facilitates myogenic differentiation of murine myoblasts by promoting membrane hyperpolarization.J Biol Chem. 2019 Sep 27;294(39):14279-14288. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008840. Epub 2019 Aug 6. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31387946 Free PMC article.
-
A biomimetic approach to modulating the sustained release of fibroblast growth factor 2 from fibrin microthread scaffolds.Explor Biomat X. 2024;1(2):58-83. doi: 10.37349/ebmx.2024.00006. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Explor Biomat X. 2024. PMID: 39070763 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Contracture of 3D Collagen Constructs by Fibronectin-Deficient Murine Fibroblasts.Front Physiol. 2019 Mar 5;10:166. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00166. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30890950 Free PMC article.
-
The Volume-Regulated Anion Channel LRRC8 is Involved in the Initiation of Epidermal Differentiation and is Deregulated in Psoriasis.JID Innov. 2025 Feb 17;5(3):100357. doi: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2025.100357. eCollection 2025 May. JID Innov. 2025. PMID: 40492178 Free PMC article.
-
The physical interaction of myoblasts with the microenvironment during remodeling of the cytoarchitecture.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45329. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045329. Epub 2012 Sep 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arcangeli A, Becchetti A. Complex functional interaction between integrin receptors and ion channels. Trends Cell Biol 16: 631–639, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

