Mapping human somatosensory cortex in individual subjects with 7T functional MRI
- PMID: 20164393
- PMCID: PMC2867563
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.01017.2009
Mapping human somatosensory cortex in individual subjects with 7T functional MRI
Abstract
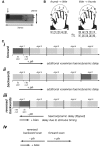
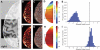
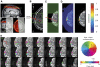
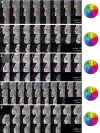
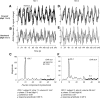
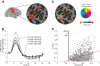
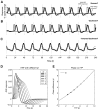
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is now routinely used to map the topographic organization of human visual cortex. Mapping the detailed topography of somatosensory cortex, however, has proven to be more difficult. Here we used the increased blood-oxygen-level-dependent contrast-to-noise ratio at ultra-high field (7 Tesla) to measure the topographic representation of the digits in human somatosensory cortex at 1 mm isotropic resolution in individual subjects. A "traveling wave" paradigm was used to locate regions of cortex responding to periodic tactile stimulation of each distal phalangeal digit. Tactile stimulation was applied sequentially to each digit of the left hand from thumb to little finger (and in the reverse order). In all subjects, we found an orderly map of the digits on the posterior bank of the central sulcus (postcentral gyrus). Additionally, we measured event-related responses to brief stimuli for comparison with the topographic mapping data and related the fMRI responses to anatomical images obtained with an inversion-recovery sequence. Our results have important implications for the study of human somatosensory cortex and underscore the practical utility of ultra-high field functional imaging with 1 mm isotropic resolution for neuroscience experiments. First, topographic mapping of somatosensory cortex can be achieved in 20 min, allowing time for further experiments in the same session. Second, the maps are of sufficiently high resolution to resolve the representations of all five digits and third, the measurements are robust and can be made in an individual subject. These combined advantages will allow somatotopic fMRI to be used to measure the representation of digits in patients undergoing rehabilitation or plastic changes after peripheral nerve damage as well as tracking changes in normal subjects undergoing perceptual learning.
Figures
References
-
- Buckner RL, Goodman J, Burock M, Rotte M, Koutstaal W, Schacter D, Rosen B, Dale AM. Functional-anatomic correlates of object priming in humans revealed by rapid presentation event-related fMRI. Neuron 20: 285–296, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Burock MA, Buckner RL, Woldorff MG, Rosen BR, Dale AM. Randomized event-related experimental designs allow for extremely rapid presentation rates using functional MRI. Neuroreport 9: 3735–3739, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Butterworth S, Francis S, Kelly E, McGlone F, Bowtell R, Sawle GV. Abnormal cortical sensory activation in dystonia: an fMRI study. Mov Disord 18: 673–682, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Darian-Smith I. Touch in primates. Annu Rev Psychol 33: 155–194, 1982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

