Matricellular protein CCN1 activates a proinflammatory genetic program in murine macrophages
- PMID: 20164416
- PMCID: PMC2832719
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902792
Matricellular protein CCN1 activates a proinflammatory genetic program in murine macrophages
Abstract
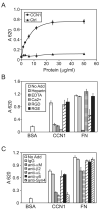
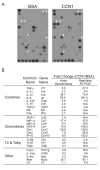
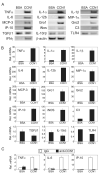
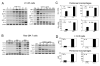
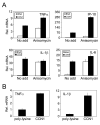
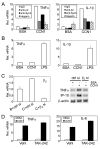
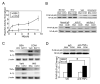
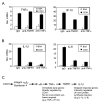
CCN1 (CYR61) is a matricellular protein that is highly expressed at sites of inflammation and wound repair. In these contexts, CCN1 can modify the activities of specific cytokines, enabling TNF-alpha to be cytotoxic without blocking NF-kappaB activity and enhancing the apoptotic activity of Fas ligand and TRAIL. In this paper, we show that CCN1 supports the adhesion of macrophages through integrin alpha(M)beta(2) and syndecan-4, activates NFkappaB-mediated transcription, and induces a proinflammatory genetic program characteristic of classically activated M1 macrophages that participates in Th1 responses. The effects of CCN1 include upregulation of cytokines (TNF-alpha, IL-1alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6, and IL-12b), chemokines (MIP-1alpha; MCP-3; growth-related oncogenes 1 and 2; and inflammatory protein 10), and regulators of oxidative stress and complement (inducible NO synthase and C3) and downregulation of specific receptors (TLR4 and IL-10Rbeta) and anti-inflammatory factors (TGF-beta1). CCN1 regulates this genetic program through at least two distinct mechanisms: an immediate-early response resulting from direct activation of NF-kappaB by CCN1, leading to the synthesis of cytokines including TNF-alpha and inflammatory protein 10; and a delayed response resulting from CCN1-induced TNF-alpha, which acts as an autocrine/paracrine mediator to activate the expression of other cytokines including IL-1beta and IL-6. These results identify CCN1 as a novel component of the extracellular matrix that activates proinflammatory genes in macrophages, implicating its role in regulating macrophage function during inflammation.
Figures
References
-
- Aszodi A, Legate KR, Nakchbandi I, Fassler R. What mouse mutants teach us about extracellular matrix function. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006;22:591. - PubMed
-
- Bornstein P, Sage EH. Matricellular proteins: extracellular modulators of cell function. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2002;14:608. - PubMed
-
- Scatena M, Liaw L, Giachelli CM. Osteopontin: a multifunctional molecule regulating chronic inflammation and vascular disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007;27:2302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

