The major locus for mouse adenovirus susceptibility maps to genes of the hematopoietic cell surface-expressed LY6 family
- PMID: 20164425
- PMCID: PMC2832721
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903363
The major locus for mouse adenovirus susceptibility maps to genes of the hematopoietic cell surface-expressed LY6 family
Abstract
Susceptibility to mouse adenovirus type 1 is associated with the major quantitative trait locus Msq1. Msq1 was originally mapped to a 13-Mb region of mouse chromosome (Chr) 15 in crosses between SJL/J and BALB/cJ inbred mice. We have now narrowed Msq1 to a 0.75-Mb interval from 74.68 to 75.43 Mb, defined by two anonymous markers, rs8259436 and D15Spn14, using data from 1396 backcross mice. The critical interval includes 14 Ly6 or Ly6-related genes, including Ly6a (encoding Sca-1/TAP), Ly6e (Sca-2/Tsa1), Ly6g (Gr-1), and gpihbp1 (GPI-anchored high-density lipoprotein-binding protein 1), as well as the gene encoding an aldosterone synthase (Cyp11b2). The Ly6 family members are attractive candidates for virus susceptibility genes because their products are GPI-anchored membrane proteins expressed on lymphoid and myeloid cells, with proposed functions in cell adhesion and cell signaling. To determine interstrain variation in susceptibility and produce additional resources for cloning Msq1, we assayed the susceptibility phenotype of four previously untested inbred mouse strains. Susceptibility of strain 129S6/SvEvTac was subsequently localized to the Ly6 complex region, using polymorphic genetic markers on Chr 15 in a population of 271 (129S6/SvEvTac x BALB/cJ)F(1) x BALB/cJ backcross mice. We identified a major 129S6/SvEvTac susceptibility allele, Msq1(129S6), on Chr 15 in the same region as Msq1(SJL). The results indicate that a major host factor in mouse adenovirus type 1 susceptibility is likely to be a member of the Ly6 gene family.
Figures
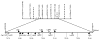
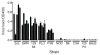

References
-
- Brinton MA. Host susceptibility to viral disease. In: Nathanson N, Ahmed R, Gonzalez-Scarano R, Griffin DE, Holmes KV, Murphy FA, Robinson HL, editors. Viral Pathogenesis. Lippincott-Raven; Philadelphia: 1997. pp. 303–328.
-
- Mashimo T, Lucas M, Simon-Chazottes D, Frenkiel MP, Montagutelli X, Ceccaldi PE, Deubel V, Guénet JL, Desprès P. A nonsense mutation in the gene encoding 2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthetase/L1 isoform is associated with West Nile virus susceptibility in laboratory mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:11311–11316. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown MG, Dokun AO, Heusel JW, Smith HRC, Beckman DL, Blattenberger EA, Dubbelde CE, Stone LR, Scalzo AA, Yokoyama WM. Vital involvement of a natural killer cell activation receptor in resistance to viral infection. Science. 2001;292:934–937. - PubMed
-
- Lee SH, Girard S, Macina D, Busa M, Zafer A, Belouchi A, Gros P, Vidal SM. Susceptibility to mouse cytomegalovirus is associated with deletion of an activating natural killer cell receptor of the C-type lectin superfamily. Nat Genet. 2001;28:42–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

