Caffeine protects against disruptions of the blood-brain barrier in animal models of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases
- PMID: 20164568
- PMCID: PMC3086010
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-2010-1376
Caffeine protects against disruptions of the blood-brain barrier in animal models of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases
Abstract
Sporadic Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD) are two of the most common neurodegenerative diseases and as such they represent major public health problems. Finding effective treatments for AD and PD represents an unmet and elusive goal largely because these diseases are chronic and progressive, and have a complicated and ill-understood pathogenesis. Although the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood, caffeine, the most commonly ingested psychoactive drug in the world, has been shown in human and animal studies to be protective against AD and PD. One mechanism implicated in the pathogenesis of AD and PD is blood-brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction and we reported recently that caffeine exerts protective effects against AD and PD at least in part by keeping the BBB intact. The present review focuses on the role of BBB dysfunction in the pathogenesis of AD and PD, caffeine's protective effects against AD and PD, and potential mechanisms whereby caffeine protects against BBB leakage.
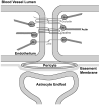
Figures

Similar articles
-
Caffeine blocks disruption of blood brain barrier in a rabbit model of Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2008 Apr 3;5:12. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-12. J Neuroinflammation. 2008. PMID: 18387175 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-brain barrier pathology in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease: implications for drug therapy.Cell Transplant. 2007;16(3):285-99. doi: 10.3727/000000007783464731. Cell Transplant. 2007. PMID: 17503739 Review.
-
Caffeine protects against MPTP-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction in mouse striatum.J Neurochem. 2008 Nov;107(4):1147-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05697.x. Epub 2008 Sep 20. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 18808450 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeine suppresses amyloid-beta levels in plasma and brain of Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2009;17(3):681-97. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2009-1071. J Alzheimers Dis. 2009. PMID: 19581723 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of aging, Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease on the blood-brain barrier transport of therapeutics.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018 Oct;135:62-74. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2018.04.009. Epub 2018 Apr 14. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018. PMID: 29665383 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Chronic Caffeine Consumption on Synaptic Function, Metabolism and Adenosine Modulation in Different Brain Areas.Biomolecules. 2023 Jan 4;13(1):106. doi: 10.3390/biom13010106. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36671491 Free PMC article.
-
Having a Coffee Break: The Impact of Caffeine Consumption on Microglia-Mediated Inflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:4761081. doi: 10.1155/2017/4761081. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 28250576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coffee, tea, and caffeine consumption and prevention of late-life cognitive decline and dementia: a systematic review.J Nutr Health Aging. 2015 Mar;19(3):313-28. doi: 10.1007/s12603-014-0563-8. J Nutr Health Aging. 2015. PMID: 25732217
-
pKr-2 induces neurodegeneration via upregulation of microglial TLR4 in the hippocampus of AD brain.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2023 Jan 18;28:100593. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2023.100593. eCollection 2023 Mar. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2023. PMID: 36798617 Free PMC article.
-
Association between tea consumption and risk of cognitive disorders: A dose-response meta-analysis of observational studies.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 27;8(26):43306-43321. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17429. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28496007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gloor SM, Wachtel M, Bolliger MF, Ishihara H, Landmann R, Frei K. Molecular and cellular permeability control at the blood-brain barrier. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001;36:258–264. - PubMed
-
- Turksen K, Troy TC. Barriers built on claudins. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:2435–2447. - PubMed
-
- Zlokovic BV. The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron. 2008;57:178–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

