Quadriceps fatigue alters human muscle performance during a novel weight bearing task
- PMID: 20164810
- PMCID: PMC2924940
- DOI: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181d85527
Quadriceps fatigue alters human muscle performance during a novel weight bearing task
Abstract
Limited information is currently available regarding muscle synergistic patterns and triggered reflex responses during dynamic weight-bearing activities in the presence of muscle fatigue.
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of quadriceps muscle fatigue on patterns of muscle activation and performance in response to sudden, unexpected perturbations during a weight-bearing task.
Methods: Motion of the knee was measured as subjects were asked to track a visual target as accurately as possible while performing a resisted single leg squat task. Random perturbations were delivered in 20% of the trials by unexpectedly releasing the resistance during the flexion phase of the exercise. Absolute and constant errors were calculated to evaluate target tracking performance. Quadriceps and hamstring muscle activity was recorded during both perturbed and unperturbed trials. Twelve healthy women were tested before and after completing a repetitive submaximal eccentric quadriceps fatigue protocol. A second group of 12 women served as controls. Unexpected perturbations elicited long-latency responses characterized by facilitation of the quadriceps and inhibition of the hamstrings.
Results: Muscle fatigue increased the amplitude of the long-latency response in vastus lateralis by 4.3% maximum voluntary isometric contraction (P = 0.004). Changes in tracking error occurred in response to perturbations after fatigue in spite of significantly increased quadriceps muscle activity, especially during the extension phase of the exercise.
Conclusion: Quadriceps muscle fatigue alters the patterns of coordinated muscle activity and may render subjects less able to cope with unexpected perturbations during weight-bearing tasks.
Figures



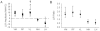


Comment in
-
Is generic physical activity or specific exercise associated with motor abilities?Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010 Sep-Oct;9(5):262. doi: 10.1249/JSR.0b013e3181f36139. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010. PMID: 20827089 No abstract available.
References
-
- Balestra C, Duchateau J, Hainaut K. Effects of fatigue on the stretch reflex in a human muscle. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1992;85(1):46–52. - PubMed
-
- Botter A, Lanfranco F, Merletti R, Minetto MA. Myoelectric fatigue profiles of three knee extensor muscles. Int J Sports Med. 2009:30408–417. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter JE, Blasier RB, Pellizzon GG. The effects of muscle fatigue on shoulder joint position sense. Am J Sports Med. 1998;26(2):262–265. - PubMed
-
- Darling WG, Hayes KC. Human servo responses to load disturbances in fatigued muscle. Brain Res. 1983;267(2):345–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

