Short- and long-term modulation of the exercise ventilatory response
- PMID: 20164813
- PMCID: PMC3022007
- DOI: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181d7b212
Short- and long-term modulation of the exercise ventilatory response
Abstract
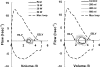
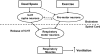
The importance of adaptive control strategies (modulation and plasticity) in the control of breathing during exercise has become recognized only in recent years. In this review, we discuss new evidence for modulation of the exercise ventilatory response in humans, specifically, short- and long-term modulation. Short-term modulation is proposed to be an important regulatory mechanism that helps maintain blood gas homeostasis during exercise.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Short-term modulation of the ventilatory response to exercise is preserved in obstructive sleep apnea.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2017 Feb;236:42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2016.11.003. Epub 2016 Nov 10. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27840272 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of locomotor muscle afferent inhibition on the ventilatory response to exercise in heart failure.Exp Physiol. 2014 Feb;99(2):414-26. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2013.075937. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Exp Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24163425 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of an airflow restriction mask (ARM) on metabolic, ventilatory, and electromyographic responses to continuous cycling exercise.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 11;15(8):e0237010. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237010. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32780739 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting dysanapsis: sex-based differences in airways and the mechanics of breathing during exercise.Exp Physiol. 2016 Feb;101(2):213-8. doi: 10.1113/EP085366. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Exp Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26440369 Review.
-
Layers of exercise hyperpnea: modulation and plasticity.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2006 Apr 28;151(2-3):251-66. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2006.02.003. Epub 2006 Mar 10. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16530024 Review.
Cited by
-
In-silico simultaneous respiratory and circulatory measurement during voluntary breathing, exercise, and mental stress: A computational approach.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 Dec 17;20(12):e1012645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012645. eCollection 2024 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 39689064 Free PMC article.
-
Passive limb training modulates respiratory rhythmic bursts.Sci Rep. 2023 May 4;13(1):7226. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34422-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37142670 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise ventilatory limitation: the role of expiratory flow limitation.Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2013 Jan;41(1):11-8. doi: 10.1097/JES.0b013e318267c0d2. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2013. PMID: 23038244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of adding CO2 to hypoxic inspired gas on cerebral blood flow velocity and breathing during incremental exercise.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 21;8(11):e81130. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081130. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24278389 Free PMC article.
-
Time Domains of the Hypoxic Ventilatory Response and Their Molecular Basis.Compr Physiol. 2016 Jun 13;6(3):1345-85. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c150026. Compr Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27347896 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agostoni E, Hyatt RE. Static behavior of the respiratory system. Handbook of Physiol. 1986:113–30.
-
- Aronson RM, Onal E, Carley DW, Lopata M. Upper ariway and respiratory muscle response to continuous negative airway pressure. Jpn.J.Physiol. 1989;66(3):1373–82. - PubMed
-
- Babb TG. Ventilatory response to exercise in subjects breathing CO2 or HeO2. J.Appl.Physiol. 1997;82:746–54. - PubMed
-
- Bach KB, Lutcavage ME, Mitchell GS. Serotonin is necessary for short-term modulation of the exercise ventilatory response. Respir.Physiol. 1993;91(1):57–70. - PubMed
-
- Baker TL, Fuller DD, Zabka AG, Mitchell GS. Respiratory plasticity: differential actions of continuous and episodic hypoxia and hypercapnia. Respir.Physiol. 2001;129(1–2):25–35. - PubMed

