Differential innate immune signalling via Ca(2+) sensor protein kinases
- PMID: 20164835
- PMCID: PMC2841715
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08794
Differential innate immune signalling via Ca(2+) sensor protein kinases
Abstract
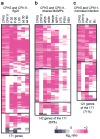
Innate immunity represents the first line of inducible defence against microbial infection in plants and animals. In both kingdoms, recognition of pathogen- or microbe-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs or MAMPs, respectively), such as flagellin, initiates convergent signalling pathways involving mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades and global transcriptional changes to boost immunity. Although Ca(2+) has long been recognized as an essential and conserved primary mediator in plant defence responses, how Ca(2+) signals are sensed and relayed into early MAMP signalling is unknown. Using a functional genomic screen and genome-wide gene expression profiling, here we show that four calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs) are Ca(2+)-sensor protein kinases critical for transcriptional reprogramming in plant innate immune signalling. Unexpectedly, CDPKs and MAPK cascades act differentially in four MAMP-mediated regulatory programs to control early genes involved in the synthesis of defence peptides and metabolites, cell wall modifications and redox signalling. Transcriptome profile comparison suggests that CDPKs are the convergence point of signalling triggered by most MAMPs. Double, triple and quadruple cpk mutant plants display progressively diminished oxidative burst and gene activation induced by the 22-amino-acid peptide flg22, as well as compromised pathogen defence. In contrast to negative roles of calmodulin and a calmodulin-activated transcription factor in plant defence, the present study reveals Ca(2+) signalling complexity and demonstrates key positive roles of specific CDPKs in initial MAMP signalling.
Figures

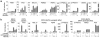
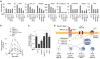
References
-
- Nurnberger T, Brunner F, Kemmerling B, Piater L. Innate immunity in plants and animals: striking similarities and obvious differences. Immunol Rev. 2004;198:249–266. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Boller T, Felix G. A renaissance of elicitors: perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2009;60:379–406. - PubMed
-
- Asai T, et al. MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature. 2002;415:977–983. - PubMed
-
- Lecourieux D, Ranjeva R, Pugin A. Calcium in plant defence-signalling pathways. New Phytol. 2006;171:249–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

