Partial calcanectomy in high-risk patients with diabetes: use and utility of a "hurricane" incisional approach
- PMID: 20165545
- PMCID: PMC2817571
Partial calcanectomy in high-risk patients with diabetes: use and utility of a "hurricane" incisional approach
Abstract
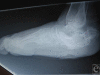
Introduction: Plantar heel ulcers in people with diabetes represent a difficult challenge to the treating physician. They become even more difficult with underlying osteomyelitis. When this infection is in the calcaneus it typically results in a partial or total calcanectomy or even more frequently, high-level amputation.
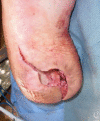
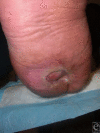
Methods: In this article, we describe a novel serpentine incisional approach to the plantar and (if necessary) posterior heel allowing for ample exposure and facilitating closure predominantly along relaxed skin tension lines.
Results: We present several representative case examples in which a hurricane incision has been used to treat and provide closure to plantar-based calcaneal ulcers.
Discussion: The use of this incision, which resembles a satellite view of a hurricane, was successful in achieving a desired partial calcanectomy and wound closure. This may be an additional tool in the armamentarium of the surgeon to assist in healing and amputation prevention.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The Vertical Contour Calcanectomy: An Alternative Surgical Technique to the Conventional Partial Calcanectomy.J Foot Ankle Surg. 2019 Mar;58(2):381-386. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2018.08.040. Epub 2019 Jan 3. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2019. PMID: 30612862 Review.
-
Partial Calcanectomy Facilitates Wound Closure of Heel Defects in High-Risk Patients.Ann Plast Surg. 2016 Jun;76(6):688-92. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000000236. Ann Plast Surg. 2016. PMID: 25003443
-
Total calcanectomy: Treatment for non-healing plantar ulcer with chronic osteomyelitis of the calcaneus.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020 Oct;11(Suppl 5):S861-S864. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2020.05.042. Epub 2020 Jun 6. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020. PMID: 32999569 Free PMC article.
-
Total calcanectomy for the treatment of chronic calcaneal osteomyelitis.Foot Ankle Int. 1998 Dec;19(12):849-55. doi: 10.1177/107110079801901210. Foot Ankle Int. 1998. PMID: 9872473
-
Outcomes of partial and total calcanectomies for the treatment of diabetic heel ulcers complicated with osteomyelitis. A systematic review and meta-analysis.Foot Ankle Surg. 2021 Aug;27(6):598-605. doi: 10.1016/j.fas.2020.07.014. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Foot Ankle Surg. 2021. PMID: 32830053
Cited by
-
Clinical characteristics, treatment and efficacy of calcaneal osteomyelitis: a systematic review with synthesis analysis of 1118 reported cases.Int J Surg. 2024 Oct 1;110(10):6810-6821. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001815. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38869983 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic limb salvage procedure with bone allograft and free flap transfer: a case report.Diabet Foot Ankle. 2017 Jan 16;8(1):1270076. doi: 10.1080/2000625X.2016.1270076. eCollection 2017. Diabet Foot Ankle. 2017. PMID: 28326158 Free PMC article.
-
Similarities and Differences Between Diabetes-Related and Trauma-Related Calcaneal Osteomyelitis: Comparisons Based on 681 Reported Cases.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Dec 8;16:7547-7557. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S437211. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 38089960 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical Treatment and Outcomes of Calcaneal Osteomyelitis in Adults: A Systematic Review.J Bone Jt Infect. 2019 May 21;4(3):146-154. doi: 10.7150/jbji.34452. eCollection 2019. J Bone Jt Infect. 2019. PMID: 31192115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singh N, Armstrong DG, Lipsky BA. Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. JAMA. 2005;293(2):217–28. - PubMed
-
- Lavery LA, Armstrong DG, Wunderlich RP, Tredwell J, Boulton AJ. Diabetic foot syndrome: evaluating the prevalence and incidence of foot pathology in Mexican Americans and non-Hispanic whites from a diabetes disease management cohort. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(5):1435–8. - PubMed
-
- Lavery LA, Armstrong DG, Wunderlich RP, Mohler MJ, Wendel CS, Lipsky BA. Risk factors for foot infections in individuals with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(6):1288–93. - PubMed
-
- Lavery LA, Peters EJG, Armstrong DG, Wendel CS, Murdoch DP, Lipsky BA. Risk factors for developing osteomyelitis in patients with diabetic foot wounds. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009;83:347–52. - PubMed
-
- Perez ML, Wagner SS, Yun J. Subtotal calcanectomy for chronic heel ulceration. J Foot Ankle Surg. 1994;33:572–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
