Treatment of diabetic vasculopathy with rosiglitazone and ramipril: Hype or hope?
- PMID: 20165647
- PMCID: PMC2822214
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-3930.54287
Treatment of diabetic vasculopathy with rosiglitazone and ramipril: Hype or hope?
Abstract
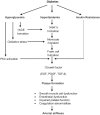
Cardiovascular diseases are responsible for increased morbidity and mortality in people with diabetes. Diabetic macrovasculopathy is associated with structural and functional changes in large arteries, which causes endothelial dysfunction, increased arterial stiffness, or decreased arterial distensability. Diabetic complications can be controlled and avoided by strict glycemic control, maintaining normal lipid profiles, regular physical exercise, adopting a healthy lifestyle and pharmacological interventions. Treatment goals for patients with type 2 diabetes specify targets for glycemia and other cardiometabolic risk factors, for example, hypertension and dyslipidemia. In recent years, special attention has been devoted to both thiazolidindiones (TZDs) and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors as clinical trials revealed that these drugs may reduce the rate of progression to diabetes or delay the onset of diabetes, regression of impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) to normoglycemia and reduces the composite of all-cause mortality, nonfatal myocardial infarction and stroke in patients with diabetes. This review focuses on the potential roles of rosiglitazone, a member of TZD class of antidiabetic agents, and ramipril, an ACE inhibitor, in preventing the preclinical macrovasculopathy in diabetes and IGT population.
Keywords: Diabetic vasculopathy; ramipril; rosiglitazone.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of rosiglitazone/ramipril on preclinical vasculopathy in newly diagnosed, untreated diabetes and IGT patients: 1-year randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2007 Aug;63(8):733-41. doi: 10.1007/s00228-007-0315-3. Epub 2007 Jun 13. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17565489 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of ramipril and of rosiglitazone on carotid intima-media thickness in people with impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose: STARR (STudy of Atherosclerosis with Ramipril and Rosiglitazone).J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009 Jun 2;53(22):2028-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.12.072. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 19477351 Clinical Trial.
-
Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus through inhibition of the Renin-Angiotensin system.Drugs. 2004;64(22):2537-65. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200464220-00004. Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15516153 Review.
-
Reduction of cardiovascular events and microvascular complications in diabetes with ACE inhibitor treatment: HOPE and MICRO-HOPE.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2002 Sep-Oct;18 Suppl 3:S82-5. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.285. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2002. PMID: 12324991 Review.
-
The HOPE Study (Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation).J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2000 Mar;1(1):18-20. doi: 10.3317/jraas.2000.002. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2000. PMID: 11967789 Review.
Cited by
-
[Update on diabetic macroangiopathy].Pathologe. 2012 May;33(3):192-204. doi: 10.1007/s00292-011-1554-8. Pathologe. 2012. PMID: 22576595 Review. German.
-
Effects of ACE inhibition on endothelial progenitor cell mobilization and prognosis after acute myocardial infarction in type 2 diabetic patients.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2013 May;68(5):665-73. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2013(05)14. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2013. PMID: 23778412 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Protective Effects and Mechanisms of Vaccarin on Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetic Angiopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 17;20(18):4587. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184587. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31533227 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roglic G, Unwin N, Bennett PH, Mathers C, Tuomilehto J, Nag S, et al. The burden of mortality attributable to diabetes: realistic estimates for the year 2000. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:2130. - PubMed
-
- IDF (2007) Fact Sheet Diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD) Available from: http://www.idf.org/home/index.cfm?node=1158 [cited in 2007]
-
- Cooper ME, Bonnet F, Oldfield M, Jandeleit-Dahm K. Mechanisms of diabetic vasculopathy: An overview. Am J Hypertens. 2001;14:475–86. - PubMed
-
- Rahman S, Rahman T, Ismail AA, Rahman AR. Diabetes-associated macrovasculopathy: Pathophysiology and pathogenesis. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism. 2007;9:767–80. - PubMed
-
- Nicolaides E, Jones CJH. Type 2 diabetes - implications for macrovascular mechanics and disease. Br J Diabetes Vasc Dis. 2002;2:9–12.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous