Pseudoaneurysm as a complication of ankle arthroscopy
- PMID: 20165687
- PMCID: PMC2822412
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5413.58614
Pseudoaneurysm as a complication of ankle arthroscopy
Abstract
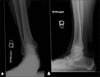
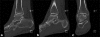
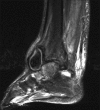
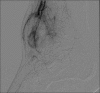
We present a case of a pseudoaneurysm of the anterior tibial artery following ankle arthroscopy with synovectomy, an extremely rare complication when standard anteromedial and anterolateral portals are used. The patient was diagnosed and treated with appropriate interventions which led to an uneventful recovery. Nevertheless, the potential sequelae of delayed diagnosis or misdiagnosis of the complication are dangerous; therefore, a high index of suspicion for a pseudoaneurysm must be maintained in the postoperative period.
Keywords: Ankle arthroscopy; anterior tibial artery; pseudoaneurysm.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mariani PP, Mancini L, Giorgini TL. Pseudoaneurysm as a complication of ankle arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 2001;17:400–2. - PubMed
-
- O'Farrell D, Dudeney S, McNally S, Moran R. Pseudoaneurysm formation after ankle arthroscopy. Foot Ankle Int. 1997;18:578–9. - PubMed
-
- van Hensbroek PB, Ponsen KJ, Reekers JA, Goslings JC. Endovascular treatment of anterior tibial artery pseudoaneurysm following locking compression plating of the tibia. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21:279–82. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton GA, Ford LA, Ceraldi C. Pseudoaneurysm after modified Lapidus arthrodesis: A case report. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2004;43:318–20. - PubMed
-
- Salgado CJ, Mukherjee D, Quist MA, Cero S. Anterior tibial artery pseudoaneurysm after ankle arthroscopy. Cardiovasc Surg. 1998;6:604–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
