The serotonin 2C receptor potently modulates the head-twitch response in mice induced by a phenethylamine hallucinogen
- PMID: 20165943
- PMCID: PMC2868321
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-010-1784-0
The serotonin 2C receptor potently modulates the head-twitch response in mice induced by a phenethylamine hallucinogen
Abstract
Rationale: Hallucinogenic serotonin 2A (5-HT(2A)) receptor partial agonists, such as (+ or -)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane hydrochloride (DOI), induce a frontal cortex-dependent head-twitch response (HTR) in rodents, a behavioral proxy of a hallucinogenic response that is blocked by 5-HT(2A) receptor antagonists. In addition to 5-HT(2A) receptors, DOI and most other serotonin-like hallucinogens have high affinity and potency as partial agonists at 5-HT(2C) receptors.
Objectives: We tested for involvement of 5-HT(2C) receptors in the HTR induced by DOI.
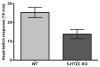
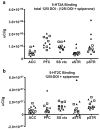
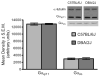
Results: Comparison of 5-HT(2C) receptor knockout and wild-type littermates revealed an approximately 50% reduction in DOI-induced HTR in knockout mice. Also, pretreatment with either the 5-HT(2C) receptor antagonist SB206553 or SB242084 eradicated a twofold difference in DOI-induced HTR between the standard inbred mouse strains C57BL/6J and DBA/2J, and decreased the DOI-induced HTR by at least 50% in both strains. None of several measures of 5-HT(2A) receptors in frontal cortex explained the strain difference, including 5-HT(2A) receptor density, Galpha(q) or Galpha(i/o) protein levels, phospholipase C activity, or DOI-induced expression of Egr1 and Egr2. 5-HT(2C) receptor density in the brains of C57BL/6J and DBA/2J was also equivalent, suggesting that 5-HT(2C) receptor-mediated intracellular signaling or other physiological modulators of the HTR may explain the strain difference in response to DOI.
Conclusions: We conclude that the HTR to DOI in mice is strongly modulated by 5-HT(2C) receptor activity. This novel finding invites reassessment of hallucinogenic mechanisms involving 5-HT(2) receptors.
Figures

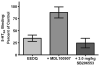


Similar articles
-
5-HT(2A) and 5-HT(2C) receptors exert opposing effects on locomotor activity in mice.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009 Jul;34(8):1958-67. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.29. Epub 2009 Mar 25. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19322172 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors in R(-)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine-elicited head twitch behavior in mice.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Dec;335(3):728-34. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.172247. Epub 2010 Sep 21. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20858706 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase C mediates (±)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI)-, but not lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)-elicited head bobs in rabbit medial prefrontal cortex.Brain Res. 2013 Jan 23;1491:98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.10.057. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23123701 Free PMC article.
-
The role of serotonin-2 (5-HT2) and dopamine receptors in the behavioral actions of the 5-HT2A/2C agonist, DOI, and putative 5-HT2C inverse agonist, SR46349B.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011 Feb;213(2-3):393-401. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-1928-2. Epub 2010 Jul 21. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011. PMID: 20652541
-
Head-twitch response in rodents induced by the hallucinogen 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine: a comprehensive history, a re-evaluation of mechanisms, and its utility as a model.Drug Test Anal. 2012 Jul-Aug;4(7-8):556-76. doi: 10.1002/dta.1333. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Drug Test Anal. 2012. PMID: 22517680 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prenatal stress induces schizophrenia-like alterations of serotonin 2A and metabotropic glutamate 2 receptors in the adult offspring: role of maternal immune system.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 16;33(3):1088-98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2331-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23325246 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of lorcaserin as an anticonvulsant in juvenile Fmr1 knockout mice.Epilepsy Res. 2021 Sep;175:106677. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2021.106677. Epub 2021 May 27. Epilepsy Res. 2021. PMID: 34130255 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT2A receptor dysregulation in a schizophrenia relevant mouse model of NMDA receptor hypofunction.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Apr 22;12(1):168. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-01930-0. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35459266 Free PMC article.
-
Natural and engineered coding variation in antidepressant-sensitive serotonin transporters.Neuroscience. 2011 Dec 1;197:28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.08.056. Epub 2011 Aug 28. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21893166 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of hallucinogenic agents mescaline and phencyclidine on zebrafish behavior and physiology.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Apr 27;37(1):194-202. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.01.003. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22251567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magelhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2004;11(7):36–42.
-
- Benedetti F, Barbini B, Bernasconi A, Fulgosi MC, Colombo C, Dallaspezia S, Gavinelli C, Marino E, Pirovano A, Radaelli D, Smeraldi E. Serotonin 5-HT2A receptor gene variants influence antidepressant response to repeated total sleep deprivation in bipolar depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008;32:1863–1866. - PubMed
-
- Benneyworth MA, Smith RL, Barrett RJ, Sanders-Bush E. Complex discriminative stimulus properties of (+)lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) in C57Bl/6J mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2005;179:854–862. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

