Understanding specific and nonspecific toxicities: a requirement for the development of dendrimer-based pharmaceuticals
- PMID: 20166124
- PMCID: PMC2905802
- DOI: 10.1002/wnan.79
Understanding specific and nonspecific toxicities: a requirement for the development of dendrimer-based pharmaceuticals
Abstract
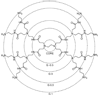
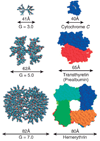
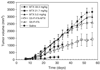
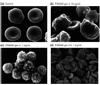
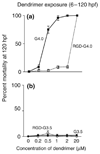
Dendrimer conjugates for pharmaceutical development are capable of enhancing the local delivery of cytotoxic drugs. The ability to conjugate different targeting ligands to the dendrimer allows for the cytotoxic drug to be focused at the intended target cell while minimizing collateral damage in normal cells. Dendrimers offer several advantages over other polymer conjugates by creating a better defined, more monodisperse therapeutic scaffold. Toxicity from the dendrimer, targeted and nonspecific, is not only dependent upon the number of targeting and therapeutic ligands conjugated, but can be influenced by the repeating building blocks that grow the dendrimer, the dendrimer generation, as well as the surface termination.
Figures

References
-
- Allen TM. Ligand-targeted therapeutics in anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:750–763. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Miyoshi H, Nakamura M. Nanomedicine for drug delivery and imaging: a promising avenue for cancer therapy and diagnosis using targeted functional nanoparticles. Int J Cancer. 2007;120:2527–2537. - PubMed
-
- Boas U, Heegaard PM. Dendrimers in drug research. Chem Soc Rev. 2004;33:43–63. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal A, Saraf S, Asthana A, Gupta U, Gajbhiye V, et al. Ligand based dendritic systems for tumor targeting. Int J Pharm. 2008;350:3–13. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal A, Asthana A, Gupta U, Jain NK. Tumour and dendrimers: a review on drug delivery aspects. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2008;60:671–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

