Synthetic and mechanistic studies on Pd(0)-catalyzed diamination of conjugated dienes
- PMID: 20166669
- PMCID: PMC2846102
- DOI: 10.1021/ja909459h
Synthetic and mechanistic studies on Pd(0)-catalyzed diamination of conjugated dienes
Abstract
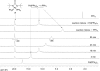
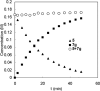
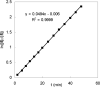
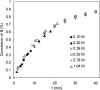
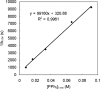
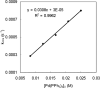
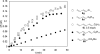
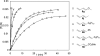
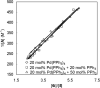
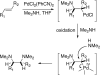
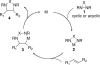
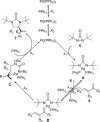
Various dienes and a triene can be regioselectively diaminated at the internal double bond with good yields and high diastereoselectivity using di-tert-butyldiaziridinone (5) as the nitrogen source and Pd(PPh(3))(4) (1-10 mol %) as the catalyst. Kinetic studies with (1)H NMR spectroscopy show that the diamination is first-order in total Pd catalyst and inverse first-order in PPh(3). For reactive dienes, such as 1-methoxybutadiene (6g) and alkyl 1,3-butadienes (6a, 6j), the diamination is first-order in di-tert-butyldiaziridinone (5) and zero-order in the olefin. For olefins with relatively low reactivity, such as (E)-1-phenylbutadiene (6b) and (3E,5E)-1,3,5-decatriene (6i), similar diamination rates were observed when 3.5 equiv of olefins were used. Pd(PPh(3))(2) is likely to be the active species for the insertion of Pd(0) into the N-N bond of di-tert-butyldiaziridinone (5) to form a four-membered Pd(II) complex (A), which can be detected by NMR spectroscopy. The olefin complex (B), formed from intermediate A via ligand exchange between the olefin substrate and the PPh(3), undergoes migratory insertion and reductive elimination to give the diamination product and regenerate the Pd(0) catalyst.
Figures


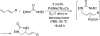
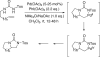
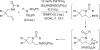
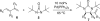
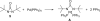
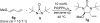
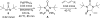

Similar articles
-
Catalytic diamination of olefins via N-N bond activation.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Dec 16;47(12):3665-78. doi: 10.1021/ar500344t. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 25402963 Free PMC article.
-
Cu(I)-catalyzed diamination of conjugated dienes. Complementary regioselectivity from two distinct mechanistic pathways involving Cu(II) and Cu(III) species.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Dec 28;133(51):20890-900. doi: 10.1021/ja207691a. Epub 2011 Dec 2. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 22081888 Free PMC article.
-
Chiral N-heterocyclic carbene--Pd(0)-catalyzed asymmetric diamination of conjugated dienes and triene.J Org Chem. 2008 Jan 18;73(2):749-51. doi: 10.1021/jo702167u. Epub 2007 Dec 21. J Org Chem. 2008. PMID: 18095707
-
Cu(I)-catalyzed regioselective diamination of conjugated dienes via dual mechanistic pathways.J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Aug 18;132(32):11009-11. doi: 10.1021/ja103838d. J Am Chem Soc. 2010. PMID: 20698659 Free PMC article.
-
The Heck reaction applied to 1,3- and 1,2-unsaturated derivatives, a way towards molecular complexity.Molecules. 2010 Apr 13;15(4):2667-85. doi: 10.3390/molecules15042667. Molecules. 2010. PMID: 20428072 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Catalytic diamination of olefins via N-N bond activation.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Dec 16;47(12):3665-78. doi: 10.1021/ar500344t. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 25402963 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Coupling of Heteroatomic Electrophiles.Chem Rev. 2019 Jul 10;119(13):8192-8228. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00628. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Chem Rev. 2019. PMID: 31184483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pd-Catalyzed Strain-Releasing Dyotropic Rearrangement: Ring-Expanding Amidofluorination of Methylenecyclobutanes.J Am Chem Soc. 2025 Mar 12;147(10):8969-8977. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5c01108. Epub 2025 Mar 2. J Am Chem Soc. 2025. PMID: 40023786 Free PMC article.
-
Cu(I)-catalyzed diamination of conjugated dienes. Complementary regioselectivity from two distinct mechanistic pathways involving Cu(II) and Cu(III) species.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Dec 28;133(51):20890-900. doi: 10.1021/ja207691a. Epub 2011 Dec 2. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 22081888 Free PMC article.
-
Cu(I)-catalyzed sequential diamination and dehydrogenation of terminal olefins: a facile approach to imidazolinones.Chemistry. 2014 Oct 20;20(43):13901-4. doi: 10.1002/chem.201404381. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Chemistry. 2014. PMID: 25213994 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
For leading reviews, see: Lucet D, Gall TL, Mioskowski C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1998;37:2580.. Mortensen MS, O'Doherty GA. Chemtracts: Org. Chem. 2005;18:555.. Kotti SRSS, Timmons C, Li G. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2006;67:101.. Kizirian J-C. Chem. Rev. 2008;108:140.. Lin G-Q, Xu M-H, Zhong Y-W, Sun X-W. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008;41:831.. de Figueiredo RM. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009;48:1190.. Cardona F, Goti A. Nat. Chem. 2009;1:269..
-
-
-
For leading references on recent Ritter-type diamination see: Li G, Kim SH, Wei H-X. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000;41:8699.. Booker-Milburn KI, Guly DJ, Cox B, Procopiou PA. Org. Lett. 2003;5:3313..
-
-
-
For examples of metal-mediated diaminations, see: Tl: Aranda VG, Barluenga J, Aznar F. Synthesis. 1974:504.. Os: Chong AO, Oshima K, Sharpless KB. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977;99:3420.. Muñiz K. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004:2243.. Hg: Barluenga J, Alonso-Cires L, Asensio G. Synthesis. 1979:962.. Co: Becker PN, White MA, Bergman RG. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980;102:5676.. Mn: Fristad WE, Brandvold TA, Peterson JR, Thompson SR. J. Org. Chem. 1985;50:3647..
-
-
-
For recent Cu(II)-mediated intramolecular diamination, see: Zabawa TP, Kasi D, Chemler SR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:11250.. Zabawa TP, Chemler SR. Org. Lett. 2007;9:2035..
-
-
-
For Rh(II), Cu(I), and Fe(III)-catalyzed diamination with TsNCl2 or TsNBr2, see: Li G, Wei H-X, Kim SH, Carducci MD. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2001;40:4277.. Wei H-X, Kim SH, Li G. J. Org. Chem. 2002;67:4777.. Han J, Li T, Pan Y, Kattuboina A, Li G. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2008;71:71..
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

