Design and application of microfluidic systems for in vitro pharmacokinetic evaluation of drug candidates
- PMID: 20166997
- PMCID: PMC3206315
- DOI: 10.2174/138920009790820093
Design and application of microfluidic systems for in vitro pharmacokinetic evaluation of drug candidates
Abstract
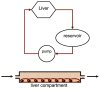
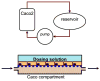
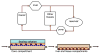
One of the fundamental challenges facing the development of new chemical entities within the pharmaceutical industry is the extrapolation of key in vivo parameters from in vitro cell culture assays and animal studies. Development of microscale devices and screening assays incorporating primary human cells can potentially provide better, faster and more efficient prediction of in vivo toxicity and clinical drug performance. With this goal in mind, large strides have been made in the area of microfluidics to provide in vitro surrogates that are designed to mimic the physiological architecture and dynamics. More recent advancements have been made in the development of in vitro analogues to physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) models - a mathematical model that represents the body as interconnected compartments specific for a particular organ. In this review we highlight recent advancements in human hepatocyte microscale culture, and describe the next generation of integrated devices, whose potential allows for the high throughput assessment of drug metabolism, distribution and pharmacokinetics.
Figures
References
-
- Chaturvedi PR, Decker CJ, Odinecs A. Prediction of pharmacokinetic properties using experimental approaches during early drug discovery. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2001;5(4):452–463. - PubMed
-
- Korfmacher WA. Lead optimization strategies as part of a drug metabolism environment. Curr Opin Drug Discov Dev. 2003;6(4):481–485. - PubMed
-
- Rathore R, Jain JP, Srivastava A, Jachak SM, Kumar N. Simultaneous determination of hydrazinocurcumin and phenol red in samples from rat intestinal permeability studies: HPLC method development and validation. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008;46(2):374–380. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell GW, Ritchie DM, Masucci JA, Hageman W, Yan Z. The new pre-preclinical paradigm: compound optimization in early and late phase drug discovery. Curr Top Med Chem. 2001;1(5):353–366. - PubMed
-
- Tang L, Khan SU, Muhammad NA. Evaluation and selection of bio-relevant dissolution media for a poorly water-soluble new chemical entity. Pharm Dev Technol. 2001;6(4):531–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

