Evaluation of statistical methods for normalization and differential expression in mRNA-Seq experiments
- PMID: 20167110
- PMCID: PMC2838869
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-94
Evaluation of statistical methods for normalization and differential expression in mRNA-Seq experiments
Abstract
Background: High-throughput sequencing technologies, such as the Illumina Genome Analyzer, are powerful new tools for investigating a wide range of biological and medical questions. Statistical and computational methods are key for drawing meaningful and accurate conclusions from the massive and complex datasets generated by the sequencers. We provide a detailed evaluation of statistical methods for normalization and differential expression (DE) analysis of Illumina transcriptome sequencing (mRNA-Seq) data.
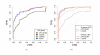
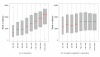
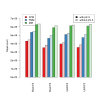
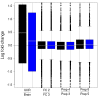
Results: We compare statistical methods for detecting genes that are significantly DE between two types of biological samples and find that there are substantial differences in how the test statistics handle low-count genes. We evaluate how DE results are affected by features of the sequencing platform, such as, varying gene lengths, base-calling calibration method (with and without phi X control lane), and flow-cell/library preparation effects. We investigate the impact of the read count normalization method on DE results and show that the standard approach of scaling by total lane counts (e.g., RPKM) can bias estimates of DE. We propose more general quantile-based normalization procedures and demonstrate an improvement in DE detection.
Conclusions: Our results have significant practical and methodological implications for the design and analysis of mRNA-Seq experiments. They highlight the importance of appropriate statistical methods for normalization and DE inference, to account for features of the sequencing platform that could impact the accuracy of results. They also reveal the need for further research in the development of statistical and computational methods for mRNA-Seq.
Figures



References
-
- Hoen PAC, Ariyurek Y, Thygesen HH, Vreugdenhil E, Vossen RHAM, de Menezes RX, Boer JM, van Ommen GJB, den Dunnen JT. Deep sequencing-based expression analysis shows major advances in robustness, resolution and inter-lab portability over five microarray platforms. Nucleic Acids Research. 2008;36(21):e141. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn705. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee A, Hansen KD, Bullard J, Dudoit S, Sherlock G. Novel low abundance and transient RNAs in yeast revealed by tiling microarrays and ultra high-throughput sequencing are not conserved across closely related yeast species. PLoS Genetics. 2008;4(12):e1000299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000299. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

