Identification of microRNAs expressed in two mosquito vectors, Aedes albopictus and Culex quinquefasciatus
- PMID: 20167119
- PMCID: PMC2834634
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-119
Identification of microRNAs expressed in two mosquito vectors, Aedes albopictus and Culex quinquefasciatus
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression in a variety of organisms, including insects, vertebrates, and plants. miRNAs play important roles in cell development and differentiation as well as in the cellular response to stress and infection. To date, there are limited reports of miRNA identification in mosquitoes, insects that act as essential vectors for the transmission of many human pathogens, including flaviviruses. West Nile virus (WNV) and dengue virus, members of the Flaviviridae family, are primarily transmitted by Aedes and Culex mosquitoes. Using high-throughput deep sequencing, we examined the miRNA repertoire in Ae. albopictus cells and Cx. quinquefasciatus mosquitoes.
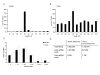
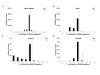
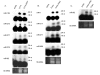
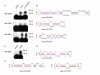
Results: We identified a total of 65 miRNAs in the Ae. albopictus C7/10 cell line and 77 miRNAs in Cx. quinquefasciatus mosquitoes, the majority of which are conserved in other insects such as Drosophila melanogaster and Anopheles gambiae. The most highly expressed miRNA in both mosquito species was miR-184, a miRNA conserved from insects to vertebrates. Several previously reported Anopheles miRNAs, including miR-1890 and miR-1891, were also found in Culex and Aedes, and appear to be restricted to mosquitoes. We identified seven novel miRNAs, arising from nine different precursors, in C7/10 cells and Cx. quinquefasciatus mosquitoes, two of which have predicted orthologs in An. gambiae. Several of these novel miRNAs reside within a ~350 nt long cluster present in both Aedes and Culex. miRNA expression was confirmed by primer extension analysis. To determine whether flavivirus infection affects miRNA expression, we infected female Culex mosquitoes with WNV. Two miRNAs, miR-92 and miR-989, showed significant changes in expression levels following WNV infection.
Conclusions: Aedes and Culex mosquitoes are important flavivirus vectors. Recent advances in both mosquito genomics and high-throughput sequencing technologies enabled us to interrogate the miRNA profile in these two species. Here, we provide evidence for over 60 conserved and seven novel mosquito miRNAs, expanding upon our current understanding of insect miRNAs. Undoubtedly, some of the miRNAs identified will have roles not only in mosquito development, but also in mediating viral infection in the mosquito host.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of mosquito microRNA Aae-miR-2940-5p is downregulated in response to West Nile virus infection to restrict viral replication.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(15):8457-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00317-14. Epub 2014 May 14. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24829359 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of MicroRNAs in the West Nile Virus Vector Culex tarsalis (Diptera: Culicidae).J Med Entomol. 2023 Mar 6;60(2):182-293. doi: 10.1093/jme/tjac182. J Med Entomol. 2023. PMID: 36477983 Free PMC article.
-
Growth characteristics of the veterinary vaccine candidate ChimeriVax-West Nile (WN) virus in Aedes and Culex mosquitoes.Med Vet Entomol. 2003 Sep;17(3):235-43. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2915.2003.00438.x. Med Vet Entomol. 2003. PMID: 12941006
-
West Nile virus: the Indian scenario.Indian J Med Res. 2003 Sep;118:101-8. Indian J Med Res. 2003. PMID: 14700342 Review.
-
Wolbachia dominance influences the Culex quinquefasciatus microbiota.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 3;13(1):18980. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46067-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37923779 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Translational regulation of Anopheles gambiae mRNAs in the midgut during Plasmodium falciparum infection.BMC Genomics. 2012 Aug 2;13:366. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-366. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22857387 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-Wide Evaluation Characterization of microRNAs and Assessment of Their Functional Roles as Regulators of Diapause in Ostrinia furnacalis Larvae (Lepidoptera: Crambidae).Insects. 2024 Sep 14;15(9):702. doi: 10.3390/insects15090702. Insects. 2024. PMID: 39336670 Free PMC article.
-
Role of microRNAs in arbovirus/vector interactions.Viruses. 2014 Sep 23;6(9):3514-34. doi: 10.3390/v6093514. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 25251636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of mosquito microRNA Aae-miR-2940-5p is downregulated in response to West Nile virus infection to restrict viral replication.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(15):8457-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00317-14. Epub 2014 May 14. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24829359 Free PMC article.
-
miR-281, an abundant midgut-specific miRNA of the vector mosquito Aedes albopictus enhances dengue virus replication.Parasit Vectors. 2014 Oct 22;7:488. doi: 10.1186/s13071-014-0488-4. Parasit Vectors. 2014. PMID: 25331963 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

