The ClpP protease homologue is required for the transmission traits and cell division of the pathogen Legionella pneumophila
- PMID: 20167127
- PMCID: PMC2838875
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-54
The ClpP protease homologue is required for the transmission traits and cell division of the pathogen Legionella pneumophila
Abstract
Background: Legionella pneumophila, the intracellular bacterial pathogen that causes Legionnaires' disease, exhibit characteristic transmission traits such as elevated stress tolerance, shortened length and virulence during the transition from the replication phase to the transmission phase. ClpP, the catalytic core of the Clp proteolytic complex, is widely involved in many cellular processes via the regulation of intracellular protein quality.
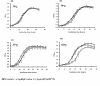
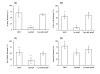
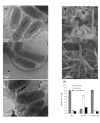
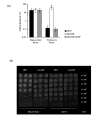
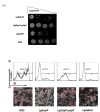
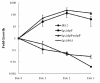
Results: In this study, we showed that ClpP was required for optimal growth of L. pneumophila at high temperatures and under several other stress conditions. We also observed that cells devoid of clpP exhibited cell elongation, incomplete cell division and compromised colony formation. Furthermore, we found that the clpP-deleted mutant was more resistant to sodium stress and failed to proliferate in the amoebae host Acanthamoeba castellanii.
Conclusions: The data present in this study illustrate that the ClpP protease homologue plays an important role in the expression of transmission traits and cell division of L. pneumophila, and further suggest a putative role of ClpP in virulence regulation.
Figures

References
-
- Fraser DW, Tsai TR, Orenstein W, Parkin WE, Beecham HJ, Sharrar RG, Harris J, Mallison GF, Martin SM, McDade JE, Shepard CC, Brachman PS. Legionnaires' disease: description of an epidemic of pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1977;297:1189–1197. - PubMed
-
- Kaufmann AF, McDade JE, Patton CM, Bennett JV, Skaliy P, Feeley JC, Anderson DC, Potter ME, Newhouse VF, Gregg MB, Brachman PS. Pontiac fever: isolation of the etiologic agent (Legionella pneumophilia) and demonstration of its mode of transmission. Am J Epidemiol. 1981;114:337–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

