Restoring catalase activity in Staphylococcus aureus subsp. anaerobius leads to loss of pathogenicity for lambs
- PMID: 20167202
- PMCID: PMC2839792
- DOI: 10.1051/vetres/2010013
Restoring catalase activity in Staphylococcus aureus subsp. anaerobius leads to loss of pathogenicity for lambs
Abstract
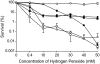
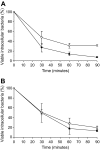
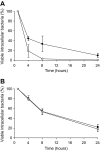
Staphylococcus aureus subsp. anaerobius, a microaerophilic and catalase-negative bacterium, is the etiological agent of abscess disease, a specific chronic condition of sheep and goats, which is characterized by formation of necrotic lesions that are located typically in superficial lymph nodes. We constructed an isogenic mutant of S. aureus subsp. anaerobius (RDKA84) that carried a repaired and functional catalase gene from S. aureus ATCC 12600, to investigate whether the lack of catalase in S. aureus subsp. anaerobius plays a role in its physiological and pathogenic characteristics. The catalase activity had no apparent influence on the in vitro growth characteristics of RDKA84, which, like the wild-type, did not grow on aerobically incubated agar plates. Restoration of catalase activity in RDKA84 substantially increased resistance to H2O2 when analyzed in a death assay. The intracellular survival rates of the catalase-positive mutant RDKA84 in polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) isolated from adult sheep were significantly higher than those of the wild-type, while no differences were found with PMN isolated from lambs. RDKA84 showed significantly lower survival rates in murine macrophages (J774A.1 cells) than the wild-type strains did, whereas, in bovine mammary epithelial cells (MAC-T), no differences in intracellular survival were observed. Interestingly, the virulence for lambs, the natural host for abscess disease, of the catalase-positive mutant RDKA84 was reduced dramatically in comparison with wild-type S. aureus subsp. anaerobius in two experimental models of infection.
Copyright (c) INRA, EDP Sciences, 2010.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simultaneous lack of catalase and beta-toxin in Staphylococcus aureus leads to increased intracellular survival in macrophages and epithelial cells and to attenuated virulence in murine and ovine models.Microbiology (Reading). 2009 May;155(Pt 5):1505-1515. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.025544-0. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Microbiology (Reading). 2009. PMID: 19383704
-
Staphylococcus aureus subsp. anaerobius isolates from different countries are clonal in nature.Vet Microbiol. 2011 May 12;150(1-2):198-202. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2010.12.022. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Vet Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21236606
-
Catalase deficiency in Staphylococcus aureus subsp. anaerobius is associated with natural loss-of-function mutations within the structural gene.Microbiology (Reading). 2000 Feb;146 ( Pt 2):465-475. doi: 10.1099/00221287-146-2-465. Microbiology (Reading). 2000. PMID: 10708385
-
The catalase gene differentiates between some strains of Staphylococcus aureus ssp. anaerobius.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2010 May;55(3):211-4. doi: 10.1007/s12223-010-0030-9. Epub 2010 Jun 6. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2010. PMID: 20526831
-
A literature review and investigation of staphylococcal necrotic dermatitis in sheep.J S Afr Vet Assoc. 2011 Dec;82(4):227-31. doi: 10.4102/jsava.v82i4.79. J S Afr Vet Assoc. 2011. PMID: 22616437 Review.
Cited by
-
PFGE and AFLP genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus subsp. anaerobius isolated from goats with Morel's disease.Arch Microbiol. 2013 Jan;195(1):37-41. doi: 10.1007/s00203-012-0844-8. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Arch Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 22976748 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus subspecies based on MALDI-TOF MS profiles.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2018 Nov;30(6):813-820. doi: 10.1177/1040638718805537. Epub 2018 Oct 3. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2018. PMID: 30280650 Free PMC article.
-
Taxonomic Diversity and Functional Traits of Soil Bacterial Communities under Radioactive Contamination: A Review.Microorganisms. 2024 Apr 3;12(4):733. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040733. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38674676 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Augustin J., Götz F., Transformation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and other staphylococcal species with plasmid DNA by electroporation, FEMS Microbiol. Lett. (1990) 54:203–207 - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F.M., Brent R., Kingston R.E., Moore D.D., Seidman J.G., Smith J.A., Struhl K., Current protocols in molecular biology, Green Publishing Associates and Wiley-Interscience, New York, NY, 1992
-
- Basu M., Czinn S.J., Blanchard T.G., Absence of catalase reduces long-term survival of Helicobacter pylori in macrophage phagosomes, Helicobacter (2004) 9:211–216 - PubMed
-
- Bruckner R., Gene replacement in Staphylococcus carnosus and Staphylococcus xylosus, FEMS Microbiol. Lett. (1997) 151:1–8 - PubMed
-
- Cabiscol E., Tamarit J., Ros J., Oxidative stress in bacteria and protein damage by reactive oxygen species, Int. Microbiol. (2000) 3:3–8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
