Comparison of current docking tools for the simulation of inhibitor binding by the transmembrane domain of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase
- PMID: 20167416
- PMCID: PMC2885586
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpc.2010.01.011
Comparison of current docking tools for the simulation of inhibitor binding by the transmembrane domain of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase
Abstract
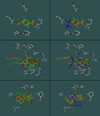
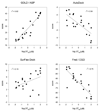
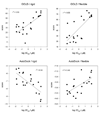
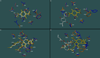
Inhibitors of the transmembrane protein sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase (SERCA) are invaluable tools for the study of the enzyme's physiological functions and they have been recognized as a promising new class of anticancer agents. For the discovery of novel enzyme inhibitors, small molecule docking for virtual screens of large compound libraries has become increasingly important. Since the performance of various docking routines varies considerably, depending on the target and the chemical nature of the ligand, we critically evaluated the performance of four frequently used programs - GOLD, AutoDock, Surflex-Dock, and FRED - for the docking of SERCA inhibitors based on the structures of thapsigargin, di-tert-butylhydroquinone, and cyclopiazonic acid. Evaluation criteria were docking accuracy using crystal structures as references, docking reproducibility, and correlation between docking scores and known bioactivities. The best overall results were obtained by GOLD and FRED. Docking runs with conformationally flexible binding sites produced no significant improvement of the results.
Figures

References
-
- Taylor RD, Jewsbury PJ, Essex JW. A review of protein-small molecule docking methods. Journal of computer-aided molecular design. 2002;16:151–166. - PubMed
-
- Lengauer T, Rarey M. Computational methods for biomolecular docking. Current opinion in structural biology. 1996;6:402–406. - PubMed
-
- Halperin I, Ma B, Wolfson H, Nussinov R. Principles of docking: An overview of search algorithms and a guide to scoring functions. Proteins. 2002;47:409–443. - PubMed
-
- Kuntz ID, Blaney JM, Oatley SJ, Langridge R, Ferrin TE. A geometric approach to macromolecule-ligand interactions. Journal of molecular biology. 1982;161:269–288. - PubMed
-
- Carlson HA, McCammon JA. Accommodating protein flexibility in computational drug design. Molecular pharmacology. 2000;57:213–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

