Novel insights into the cellular mechanisms of the anti-inflammatory effects of NF-kappaB essential modulator binding domain peptides
- PMID: 20167598
- PMCID: PMC2859510
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.099895
Novel insights into the cellular mechanisms of the anti-inflammatory effects of NF-kappaB essential modulator binding domain peptides
Abstract
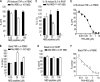
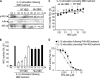
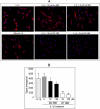
The classical nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) signaling pathway is under the control of the IkappaB kinase (IKK) complex, which consists of IKK-1, IKK-2, and NF-kappaB essential modulator (NEMO). This complex is responsible for the regulation of cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. Dysregulation of this pathway is associated with several human diseases, and as such, its inhibition offers an exciting opportunity for therapeutic intervention. NEMO binding domain (NBD) peptides inhibit the binding of recombinant NEMO to IKK-2 in vitro. However, direct evidence of disruption of this binding by NBD peptides in biological systems has not been provided. Using a cell system, we expanded on previous observations to show that NBD peptides inhibit inflammation-induced but not basal cytokine production. We report that these peptides cause the release of IKK-2 from an IKK complex and disrupt NEMO-IKK-2 interactions in cells. We demonstrate that by interfering with NEMO-IKK-2 interactions, NBD peptides inhibit IKK-2 phosphorylation, without affecting signaling intermediates upstream of the IKK complex of the NF-kappaB pathway. Furthermore, in a cell-free system of IKK complex activation by TRAF6 (TNF receptor-associated factor 6), we show that these peptides inhibit the ability of this complex to phosphorylate downstream substrates, such as p65 and inhibitor of kappaB alpha (IkappaB alpha). Thus, consistent with the notion that NEMO regulates IKK-2 catalytic activity by serving as a scaffold, appropriately positioning IKK-2 for activation by upstream kinase(s), our findings provide novel insights into the molecular mechanisms by which NBD peptides exert their anti-inflammatory effects in cells.
Figures



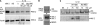
Similar articles
-
Novel non-peptide small molecules preventing IKKβ/NEMO association inhibit NF-κB activation in LPS-stimulated J774 macrophages.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Mar 15;104:83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.01.008. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26776306
-
NEMO-binding domains of both IKKalpha and IKKbeta regulate IkappaB kinase complex assembly and classical NF-kappaB activation.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 2;284(40):27596-608. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.047563. Epub 2009 Aug 7. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19666475 Free PMC article.
-
The IkappaB kinase (IKK) inhibitor, NEMO-binding domain peptide, blocks osteoclastogenesis and bone erosion in inflammatory arthritis.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 3;279(36):37219-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C400258200. Epub 2004 Jul 13. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15252035
-
Insights into targeting NEMO for pharmacological regulation.Curr Drug Targets. 2014;15(9):874-87. doi: 10.2174/1389450115666140804215119. Curr Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 25090986 Review.
-
Use of cell permeable NBD peptides for suppression of inflammation.Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Nov;65 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):iii75-82. doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.058438. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. PMID: 17038479 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-Permeable Bicyclic Peptidyl Inhibitors against NEMO-IκB Kinase Interaction Directly from a Combinatorial Library.J Am Chem Soc. 2018 Sep 26;140(38):12102-12110. doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b06738. Epub 2018 Sep 11. J Am Chem Soc. 2018. PMID: 30176143 Free PMC article.
-
Development of novel NEMO-binding domain mimetics for inhibiting IKK/NF-κB activation.PLoS Biol. 2018 Jun 11;16(6):e2004663. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2004663. eCollection 2018 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2018. PMID: 29889904 Free PMC article.
-
BHDPC Is a Novel Neuroprotectant That Provides Anti-neuroinflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects by Inactivating NF-κB and Activating PKA/CREB.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jun 25;9:614. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00614. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29988625 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects between Modified Citrus Pectin and Honokiol.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:8379843. doi: 10.1155/2017/8379843. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28900464 Free PMC article.
-
Ganoderma lucidum ethanol extract inhibits the inflammatory response by suppressing the NF-κB and toll-like receptor pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells.Exp Ther Med. 2013 Mar;5(3):957-963. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.895. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Exp Ther Med. 2013. PMID: 23408713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayden M. S., Ghosh S. (2008) Cell 132, 344–362 - PubMed
-
- Chen Z., Hagler J., Palombella V. J., Melandri F., Scherer D., Ballard D., Maniatis T. (1995) Genes Dev. 9, 1586–1597 - PubMed
-
- Karin M., Greten F. R. (2005) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5, 749–759 - PubMed
-
- Rushe M., Silvian L., Bixler S., Chen L. L., Cheung A., Bowes S., Cuervo H., Berkowitz S., Zheng T., Guckian K., Pellegrini M., Lugovskoy A. (2008) Structure 16, 798–808 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

